Using body mass index to estimate individualised patient radiation dose in abdominal computed tomography
- PMID: 30483977
- PMCID: PMC6258803
- DOI: 10.1186/s41747-018-0070-5
Using body mass index to estimate individualised patient radiation dose in abdominal computed tomography
Abstract
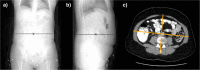
Background: The size-specific dose estimate (SSDE) is a dose-related metrics that incorporates patient size into its calculation. It is usually derived from the volume computed tomography dose index (CTDIvol) by applying a conversion factor determined from manually measured anteroposterior and lateral skin-to-skin patient diameters at the midslice level on computed tomography (CT) localiser images, an awkward, time-consuming, and not highly reproducible technique. The objective of this study was to evaluate the potential for the use of body mass index (BMI) as a size-related metrics alternative to the midslice effective diameter (DE) to obtain a size-specific dose (SSDE) in abdominal CT.
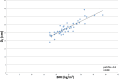
Methods: In this retrospective study of patients who underwent abdominal CT for the investigation of inflammatory bowel disease, the DE was measured on the midslice level on CT-localiser images of each patient. This was correlated with patient BMI and the linear regression equation relating the quantities was calculated. The ratio between the internal and the external abdominal diameters (DRATIO) was also measured to assess correlation with radiation dose. Pearson correlation analysis and linear regression models were used.
Results: There was good correlation between DE and patient BMI (r = 0.88). An equation allowing calculation of DE from BMI was calculated by linear regression analysis as follows: DE = 0.76 (BMI) + 9.4. A weak correlation between radiation dose and DRATIO was demonstrated (r = 0.45).
Conclusions: Patient BMI can be used to accurately estimate DE, obviating the need to measure anteroposterior and lateral diameters in order to calculate a SSDE for abdominal CT.
Keywords: Abdomen; Body mass index; Radiation dosage; Tomography (x-ray, computed).
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Approval for this study was granted by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the Cork Teaching Hospitals, Lancaster Hall, 6 Little Hanover Street, Cork, Ireland. Informed consent was obtained from each patient.
Consent for publication
The consent for publication is included in the informed consent.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- Brenner David J., McCollough Cynthia H., Orton Colin G. It is time to retire the computed tomography dose index (CTDI) for CT quality assurance and dose optimization. Medical Physics. 2006;33(5):1189–1191. - PubMed
-
- American Association of Physicists in Medicine (2011) Size-specific dose estimates (SSDE) in pediatric and adult body CT examinations (Report 204). https://www.aapm.org/pubs/reports/RPT_204.pdf. Accessed Sept 22 2018
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
