Interventions for preventing intensive care unit delirium in adults
- PMID: 30484283
- PMCID: PMC6373634
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD009783.pub2
Interventions for preventing intensive care unit delirium in adults
Abstract
Background: Delirium is defined as a disturbance in attention, awareness and cognition with reduced ability to direct, focus, sustain and shift attention, and reduced orientation to the environment. Critically ill patients in the intensive care unit (ICU) frequently develop ICU delirium. It can profoundly affect both them and their families because it is associated with increased mortality, longer duration of mechanical ventilation, longer hospital and ICU stay and long-term cognitive impairment. It also results in increased costs for society.
Objectives: To assess existing evidence for the effect of preventive interventions on ICU delirium, in-hospital mortality, the number of delirium- and coma-free days, ventilator-free days, length of stay in the ICU and cognitive impairment.
Search methods: We searched CENTRAL, MEDLINE, Embase, BIOSIS, International Web of Science, Latin American Caribbean Health Sciences Literature, CINAHL from 1980 to 11 April 2018 without any language limits. We adapted the MEDLINE search for searching the other databases. Furthermore, we checked references, searched citations and contacted study authors to identify additional studies. We also checked the following trial registries: Current Controlled Trials; ClinicalTrials.gov; and CenterWatch.com (all on 24 April 2018).
Selection criteria: We included randomized controlled trials (RCTs) of adult medical or surgical ICU patients receiving any intervention for preventing ICU delirium. The control could be standard ICU care, placebo or both. We assessed the quality of evidence with GRADE.
Data collection and analysis: We checked titles and abstracts to exclude obviously irrelevant studies and obtained full reports on potentially relevant ones. Two review authors independently extracted data. If possible we conducted meta-analyses, otherwise we synthesized data narratively.
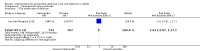
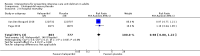
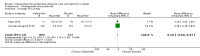
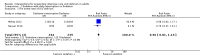
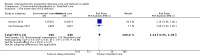
Main results: The electronic search yielded 8746 records. We included 12 RCTs (3885 participants) comparing usual care with the following interventions: commonly used drugs (four studies); sedation regimens (four studies); physical therapy or cognitive therapy, or both (one study); environmental interventions (two studies); and preventive nursing care (one study). We found 15 ongoing studies and five studies awaiting classification. The participants were 48 to 70 years old; 48% to 74% were male; the mean acute physiology and chronic health evaluation (APACHE II) score was 14 to 28 (range 0 to 71; higher scores correspond to more severe disease and a higher risk of death). With the exception of one study, all participants were mechanically ventilated in medical or surgical ICUs or mixed. The studies were overall at low risk of bias. Six studies were at high risk of detection bias due to lack of blinding of outcome assessors. We report results for the two most commonly explored approaches to delirium prevention: pharmacologic and a non-pharmacologic intervention.Haloperidol versus placebo (two RCTs, 1580 participants)The event rate of ICU delirium was measured in one study including 1439 participants. No difference was identified between groups, (risk ratio (RR) 1.01, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.87 to 1.17) (moderate-quality evidence). Haloperidol versus placebo neither reduced or increased in-hospital mortality, (RR 0.98, 95% CI 0.80 to 1.22; 2 studies; 1580 participants (moderate-quality evidence)); the number of delirium- and coma-free days, (mean difference (MD) -0.60, 95% CI -1.37 to 0.17; 2 studies, 1580 participants (moderate-quality of evidence)); number of ventilator-free days (mean 23.8 (MD -0.30, 95% CI -0.93 to 0.33) 1 study; 1439 participants, (high-quality evidence)); length of ICU stay, (MD 0.18, 95% CI -0.60 to 0.97); 2 studies, 1580 participants; high-quality evidence). None of the studies measured cognitive impairment. In one study there were three serious adverse events in the intervention group and five in the placebo group; in the other there were five serious adverse events and three patients died, one in each group. None of the serious adverse events were judged to be related to interventions received (moderate-quality evidence).Physical and cognitive therapy interventions (one study, 65 participants)The study did not measure the event rate of ICU delirium. A physical and cognitive therapy intervention versus standard care neither reduced nor increased in-hospital mortality, (RR 0.94, 95% CI 0.40 to 2.20, I² = 0; 1 study, 65 participants; very low-quality evidence); the number of delirium- and coma-free days, (MD -2.8, 95% CI -10.1 to 4.6, I² = 0; 1 study, 65 participants; very low-quality evidence); the number of ventilator-free days (within the first 28/30 days) was median 27.4 (IQR 0 to 29.2) and 25 (IQR 0 to 28.9); 1 study, 65 participants; very low-quality evidence, length of ICU stay, (MD 1.23, 95% CI -0.68 to 3.14, I² = 0; 1 study, 65 participants; very low-quality evidence); cognitive impairment measured by the MMSE: Mini-Mental State Examination with higher scores indicating better function, (MD 0.97, 95% CI -0.19 to 2.13, I² = 0; 1 study, 30 participants; very low-quality evidence); or measured by the Dysexecutive questionnaire (DEX) with lower scores indicating better function (MD -8.76, 95% CI -19.06 to 1.54, I² = 0; 1 study, 30 participants; very low-quality evidence). One patient experienced acute back pain accompanied by hypotensive urgency during physical therapy.
Authors' conclusions: There is probably little or no difference between haloperidol and placebo for preventing ICU delirium but further studies are needed to increase our confidence in the findings. There is insufficient evidence to determine the effects of physical and cognitive intervention on delirium. The effects of other pharmacological interventions, sedation, environmental, and preventive nursing interventions are unclear and warrant further investigation in large multicentre studies. Five studies are awaiting classification and we identified 15 ongoing studies, evaluating pharmacological interventions, sedation regimens, physical and occupational therapy combined or separately, and environmental interventions, that may alter the conclusions of the review in future.
Conflict of interest statement
Suzanne Forsyth Herling: none known
Ingrid E Greve: none known
Eduard E Vasilevskis was supported by Award Number K23AG040157 from the National Institute On Aging. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institute On Aging or the National Institutes of Health see Sources of support. Dr Vasilevskis has also received support for an educational presentation in a topical area relevant to the review. (ICU Mortality Reduction Collaborative. CareFusion Center for Safety and Excellence. ABCDEs of delirium prevention. October 2011.) The content does not reflect the views of the funding body of this educational presentation.
Ingrid Egerod: none known.
Camilla Bekker Mortensen: none known.
Ann Merete Møller: none known.
Helle Svenningsen's PhD study (2009 to 2012) on delirium was supported by several foundations: the Novo Nordics Foundation; Foundation for Psychiatry's encouraging, Risskov; Foundation for Psychiatry's encouraging, Risskov; Region Midts Health Research Foundation;Fundation of Research in Mental Disorders, Aarhus University; Danish Society for Nursing Research; Lippmann Foundation; Færgemans scholarship; Foundation of Psychiatry promotion. None of the foundations had any influence on this review.
Thordis Thomsen: none known.
Figures
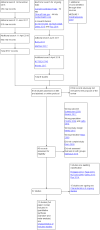









Update of
References
References to studies included in this review
Abdelgalel 2016 {published data only}
-
- Abdelgalel EF. Dexmedetomidine versus haloperidol for prevention of delirium during non‐invasive mechanical ventilation. Egyptian Journal of Anaesthesia 2016;32(4):473‐81. [DOI: 10.1016/j.egja.2016.05.008] - DOI
Brummel 2014b {published data only}
-
- Brummel NE, Girard TD, Ely EW, Pandhariphande PP, Morandi A, Hughes CG, et al. Feasibility and safety of early combined cognitive and physical therapy for critically ill medical and surgical patients: the Activity and cognitive Therapy in ICU (ACT‐ICU) trial. Intensive Care Medicine 2014;40(3):370‐9. [DOI: 10.1007/s00134-013-3136-0; PUBMED: 24257969 ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Mehta 2012 {published data only}
-
- Mehta S, Burry L, Cook D, Fergusson D, Steinberg M, Granton, et al. Daily sedation interruption in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients cared for with a sedation protocol: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2012;308(19):1985‐92. [PUBMED: 23180503] - PubMed
Moon 2015 {published data only}
-
- Moon KJ, Lee SM. The effects of a tailored intensive care unit delirium prevention protocol : A randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2015;52(9):1423‐32. [PUBMED: 26032729] - PubMed
Nassar 2014 {published data only}
Page 2013 {published data only}
-
- Page VJ, Ely EW, Gates S, Zhao XB, Alce T, Shintani A, et al. Effect of intravenous haloperidol on the duration of delirium and coma in critically ill patients (HOPE‐ICU): a randomised, double‐blind, placebo‐controlled trial. The Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2013;1(7):515‐23. [PUBMED: 24461612 ] - PMC - PubMed
Pandharipande 2007 {published data only}
-
- Pandharipande PP, Pun BT, Herr DL, Maze M, Girard TD, Miller RR, et al. Effect of sedation with dexmedetomidine vs lorazepam on acute brain dysfunction in mechanically ventilated patients: the MENDS randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2007;298(22):2644‐53. [PUBMED: 18073360] - PubMed
Shehabi 2013 {published data only}
-
- Shehabi Y, Bellomo R, Reade MC, Bailey M, Bass F, Howe B, et al. Early goal‐directed sedation versus standard sedation in mechanically ventilated critically ill patients: A pilot study. Critical Care Medicine 2013;41(8):1983‐91. [PUBMED: 23863230] - PubMed
Simons 2016 {published data only}
-
- Simons KS, Laheij RF, Boogaard M, Moviat MM, Paling AJ, Polderman FN, et al. Dynamic light application therapy to reduce the incidence and duration of delirium in intensive‐care patients : a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respiratory 2016;4(3):194‐202. [PUBMED: 26895652] - PubMed
Strøm 2010 {published data only}
-
- Strøm T, Martinussen T, Toft P. A protocol of no sedation for critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation: a randomised trial. Lancet 2010;375(9713):475‐80. [PUBMED: 20116842] - PubMed
Van Den Boogard 2018 {published data only}
Van Rompaey 2012 {published data only}
References to studies excluded from this review
Álvarez 2017 {published data only}
-
- Álvarez EA, Garrido MA, Tobar EA, Prieto SA, Vergara SO, Briceno CD, et al. Occupational therapy for delirium management in elderly patients without mechanical ventilation in an intensive care unit : A pilot randomized clinical trial. Journal of Critical Care 2017;37:85‐90. [PUBMED: 27660922 ] - PubMed
Esen 2009 {unpublished data only}
-
- Esen F, Senturk E, Erginzcan P, Kiraner E, Dogruel B, Disci R, et al. Effect of magnesium on sepsis associated delirium. 29th International Symposium on Intensive Care and Emergency Medicine Brussels Belgium. 24.03 2009‐27.03.2009.
Finotto 2006 {published data only}
-
- Finotto S, Artioli G, Davoli L, Barbara B. Nursing interventions for the prevention of the delirium in intensive care unit (ICU): A randomized study [Interventi infermieristici nella prevenzione del delirium in Unita Coronarica: uno studio randomizzata]. Professioni Infermieristiche 2006;59(4):228‐32. [PUBMED: 17320017] - PubMed
Hatta 2014 {published data only}
-
- Hatta K, Kishi Y, Wada K, Takeuchi T, Odawara T, Usui C, et al. Preventive effects of ramelteon on delirium a randomized placebo‐controlled trial. JAMA Psychiatry 2016;71(4):397‐403. [PUBMED: 24554232] - PubMed
Mansouri 2016 {published data only}
-
- Mansouri P, Javadpour S, Zand F, Ghodsbin F, Sabetian G, Masjedi M, et al. Implementation of a protocol for integrated management of pain, agitation, and delirium can improve clinical outcomes in the intensive care unit: A randomized clinical trial. Journal of Critical Care 2016;28(6):918‐22. [PUBMED: 24011845] - PubMed
Mehta 2015 {published data only}
-
- Mehta S, Cook D, Devlin JW, Skrobik Y, Meade M, Fergusson D, et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and outcomes of delirium in mechanically ventilated adults. Critical Care Medicine 2015;43(3):557‐66. [PUBMED: 25493968] - PubMed
Riker 2009 {published data only}
-
- Riker RR, Shehabi Y, Bokesch PM, Ceraso D, Wisemandle W, Koura F, et al. Dexmedetomidine vs midazolam for sedation of critically ill patients. JAMA 2009;301(5):489‐99. [PUBMED: 19188334] - PubMed
Schweickert 2009 {published data only}
-
- Schweickert WD, Pohlman MC, Pohlman AS, Nigos C, Pawlik AJ, Esbrook CL, et al. Early physical and occupational therapy in mechanically ventilated, critically ill patients: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009;373(9678):1874‐882. [DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60658-9; PUBMED: 19446324] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
References to studies awaiting assessment
Daley 2015 {unpublished data only}
-
- Daley B. Dexmedetomidine versus propofol prolonged sedation in critically ill trauma and surgical patients. http://clinicaltrails.gov/show/NCT02548923. [NCT02548923] - PubMed
NCT02612948 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Quetiapine for delirium prophylaxis in high‐risk critically ill patients. http://cninicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02612948 2014. [NCT02612948] - PubMed
Page 2015 {published data only}
-
- Page VJ, Marti J, McAuley DF, Casarin A, Alce T, Zhao XB, et al. Health evaluation and cost‐effectiveness analysis from a randomized trial of haloperidol in the management of delirium in the critically ill (hope‐ICU trial). American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2015:191.
Preslaski 2012 {published data only}
-
- Preslaski C, Mueller S, Kiser T, Fish D, MacLaren R. Dexmedetomidine vs. midazolam for facilitating extubation in medical and surgical ICU patients: A randomized, double‐blind study. Critical Care Medicine. December; Vol. 1:281.
Ryu 2014 {unpublished data only}
-
- Ryu H. Efficacy of Low‐dose Dexmedetomidine to prevent delirium in liver transplant patients. http: //clinicaltrials.gov.gov/ct2/show/NCT02245256.
References to ongoing studies
Burry 2017 {published data only}
Jerath 2015 {published data only}
Martinez 2017 {published data only}
Miles 2012 {published data only}
-
- Miles M, Hite RD. A randomized controlled trial of direct noise reduction in the ICU. Journal of Investigative Medicine. January 2012; Vol. 60:455.
NCT01739933 {published data only}
-
- NCT01739933. The MENDSII study, maximizing the efficacy of sedation and reducing neurological dysfunction and mortality in septic patients with acute respiratory failure (MENDSII). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT01739933?term=01739933&rank=1 first received 4 December 2012. - PMC - PubMed
NCT01791296 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT01791296. Does nightly dexmedetomidine improve sleep and reduce delirium in ICU patients? (SKY‐DEX). clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT01791296 Date first received February 12, 2013. [NCT01791296]
NCT02932358 {published and unpublished data}
-
- NCT02932358. Effectiveness and safety of a flexible family visitation model in adult intensive care units: a cluster‐randomized, crossover trial (The ICU Visits Study). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT02932358 First received 13 October 2016.
NCT03095443 {published data only}
-
- NCT03095443. Decreasing delirium through music (DDM). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03095443 first received 29 March 2017.
NCT03125252 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT03125252. Impact of non‐pharmacological prevention measures on the incidence of delirium in adult intensive care units. clinicaltrials.gov/show/NCT03125252 first received: 5 March 2017. [NCT03125252]
NCT03215745 {unpublished data only}
-
- NCT03215745. Delirium prevention in patients from the intensive care Uunit (DELA) (DELA). https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT03215745 first received 12 July 2017. [NCT03215745 ]
Nedergaard 2016 {published data only}
-
- Nedergaard HK, Jensen HI, Stylsvig M, Lauridsen JT, Toft P. Non‐sedation versus sedation with a daily wake‐up trial in critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation ‐ effects on long‐term cognitive function: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial, a sub study of the NONSEDA trial. Trials 2016;16(310):1‐8. [PUBMED: 26201718 ] - PMC - PubMed
Nickels 2017 {published data only}
Thomas 2015 {published data only}
-
- Thomas K, Wright SE, Watson G, Baker C, Stafford V, Wade C, et al. Extra Physiotherapy in Critical Care (EPICC) Trial Protocol: a randomised controlled trial of intensive versus standard physical rehabilitation therapy in the critically ill. BMJ Open 2015;5(1):1‐12. [PUBMED: 26009576] - PMC - PubMed
Toft 2014 {published data only}
-
- Toft P, Olsen HT, Jørgensen HK, Strøm T, Nibro HL, Oxlund J, et al. Non‐sedation versus sedation with a daily wake‐up trial in critically ill patients receiving mechanical ventilation (NONSEDA Trial): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials 2014;15(499):1‐11. [PUBMED: 25528350 ] - PMC - PubMed
Wassenaar 2017 {published data only (unpublished sought but not used)}
-
- Wassenaar A, Rood P, Schoonhoven L, Teerenstra S, Zegers M, Pickkers P, et al. International Journal of Nursing Studies The impact of nUrsiNg DEliRium Preventive INnterventions in the Intensive Care Unit (UNDERPIN‐ICU): A study protocol for a multi‐centre, stepped wedge randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2017;68(Epub 2016 Dec 8):1‐8. [PUBMED: 28013104 ] - PubMed
Additional references
Al‐Qadheeb 2014
-
- Al‐Qadheeb NS, Balk EM, Fraser GL, Skrobik Y, Riker RR, Kress JP, et al. Randomized ICU trials do not demonstrate an association between interventions that reduce delirium duration and short‐term mortality: a systematic review and meta‐analysis. Critical Care Medicine 2014;42(6):1442‐54. [PUBMED: 24557420] - PMC - PubMed
American Psychiatric Association 2000
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental disorders DSM‐IV‐TR. 4th Edition. Washington DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
American Psychiatric Association 2013
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 5th Edition. American Psychiatric Association, 2013.
Bannon 2016
-
- Bannon L, Mcgaughey J, Clarke M, Mcauley DF, Blackwood B. Impact of non‐pharmacological interventions on prevention and treatment of delirium in critically ill patients : protocol for a systematic review of quantitative and qualitative research. Systematic Reviews 2016;5(75):1‐9. [PUBMED: 27146132] - PMC - PubMed
Barbateskovic 2016
Bergeron 2001
Black 2013
-
- Black N. Patient reported outcome measures could help transform healthcare. BMJ 2013;346:167. [PUBMED: 23358487 ] - PubMed
Brummel 2012
-
- Brummel NE, Jackson JC, Girard TD, Pandharipande PP, Schiro E, Work B, et al. A combined early cognitive and physical rehabilitation program for people who are critically ill: the activity and cognitive therapy in the intensive care unit (ACT‐ICU) trial.. Physical Therapy 2012;92(12):1580‐92. [PUBMED: 22577067 ] - PMC - PubMed
Brummel 2014a
-
- Brummel NE, Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, Thompson JL, Shintani AK, Dittus RS, et al. Delirium in the ICU and subsequent long‐term disability among survivors of mechanical ventilation. Critical Care Medicine 2014;42(2):369‐377. [DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0b013e3182a645bd.; PUBMED: 24158172 ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Burry 2015
-
- Burry L, Cook D, Herridge M, Devlin JW, Fergusson D, Meade M, et al. Recall of ICU stay in patients managed with a sedation protocol or a sedation protocol with daily interruption. Critical Care Medicine 2015;43(10):2180‐90. [PUBMED: 26181221] - PubMed
Burry 2016
-
- Burry LD, Hutton B, Guenette M, Williamson D, Mehta S, Egerod I, et al. Comparison of pharmacological and non‐pharmacological interventions to prevent delirium in critically ill patients : a protocol for a systematic review incorporating network meta‐analyses. Systematic Reviews 2016;5(153):1‐8. [PUBMED: 27609018 ] - PMC - PubMed
Burry 2018
Collinsworth 2016
Davydow 2008
Devlin 2008
-
- Devlin JW, Fong JJ, Howard EP, Skrobik Y, McCoy N, Yasuda C, et al. Assessment of delirium in the intensive care unit: nursing practices and perceptions. American Journal of Critical Care 2008;17(6):555‐65. [PUBMED: 18978240 ] - PubMed
Doiron 2018
Elliott 2014
Ely 2001a
Ely 2001b
-
- Ely EW, Margolin R, Francis J, May L, Truman B, Dittus R, et al. Evaluation of delirium in critically ill patients: Validation of the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM‐ICU). Critical Care Medicine 2001;29(7):1370‐9. [PUBMED: 11445689] - PubMed
Ely 2001c
-
- Ely EW, Inouye SK, Bernard GR, Gordon S, Francis J, May L, et al. Delirium in mechanically ventilated patients: validity and reliability of the Confusion Assessment Method for the Intensive Care Unit (CAM‐ICU). JAMA 2001;286(21):2703‐10. [DOI: 10.1001/jama.286.21.2703; PUBMED: 11730446] - DOI - PubMed
Ely 2004
-
- Ely EW, Shintani A, Truman B, Speroff T, Gordon SM, Harell FE, et al. Delirium as a predictor of mortality in mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care unit. JAMA 2004;291(14):1753‐62. [PUBMED: 15082703] - PubMed
Foster 2016
Fraser 2013
-
- Fraser GL, Devlin JW, Worby CP, Alhazzani W, Barr J, Dasta JF, et al. Benzodiazepine versus nonbenzodiazepine‐based sedation for mechanically ventilated, criticallyill adults: a systematic review and meta‐analysis of randomized trials. Critical Care medicine 2013;41(9):30‐8. [PUBMED: 23989093] - PubMed
Girard 2010
GRADEpro [Computer program]
-
- GRADE Working Group, McMaster University. GRADEpro GDT. Version accessed October 2017. Hamilton (ON): GRADE Working Group, McMaster University, 2014.
Griffiths 2007
-
- Griffiths RD, Jones C. Delirium, cognitive dysfunction and posttraumatic stress disorder. Current Opinion in Anaesthesiology 2007;20(2):124‐9. [PUBMED: 17413395] - PubMed
Gusmao‐Flores 2012
-
- Gusmao‐Flores D, Ibrain J, Salluh F, Chalhub RÁ, Quarantini LC. The confusion assessment method for the intensive care unit (CAM‐ICU ) and intensive care delirium screening checklist (ICDSC) for the diagnosis of delirium : a systematic review and meta‐analysis of clinical studies. Critical Care 2012;16(4):R115. [PUBMED: 22759376] - PMC - PubMed
Guyatt 2008
Haidich 2010
Hayhurst 2016
Higgins 2011
-
- Higgins JP, Green S, (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Hu 2015
Jackson 2009
-
- Jackson JC, Mitchell N, Hopkins RO. Cognitive functioning, mental health, and quality of life in ICU survivors: an overview. Critical Care Clinics 2009;25(3):615‐28. [PUBMED: 19576534 ] - PubMed
Jackson 2014
-
- Jackson JC, Pandharipande PP, Girard TD, Brummel NE, Thompson JL, Hughes CG, et al. Depression, post‐traumatic stress disorder, and functional disability in survivors of critical illness in the BRAIN‐ICU study: a longitudinal cohort study. Lancet Respiratory Medicine 2014;2(5):369‐79. [DOI: 10.1016/S2213-2600(14)70051-7; PUBMED: 24815803] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Lan 1983
-
- Lan KG, DeMets DL. Discrete sequential boundaries for clinical trials. Biometrika 1983;70(3):659‐63.
Lonergan 2009
Luetz 2010
-
- Luetz A, Heymann A, Radtke FM, Chenitir C, Neuhaus U, Nachtigall I, et al. Different assessment tools for intensive care unit delirium: Which score to use?. Critical Care Medicine 2010;38(2):409‐18. [PUBMED: 20029345] - PubMed
Mac Sweeney 2010
-
- Mac Sweeney R, Barber V, Page V, Ely EW, Perkins GD, Young JD, et al. A national survey of the management of delirium in UK intensive care units. QJM: monthly journal of the Association of Physicians 2010;103(4):243‐51. [PUBMED: 20139102 ] - PubMed
Maldonado 2008
-
- Maldonado JR. Delirium in the acute care setting: characteristics, diagnosis and treatment. Critical Care Clinics 2008;24(4):657‐722. [PUBMED: 18929939] - PubMed
Milbrandt 2004
Miller 2006
-
- Miller RR, Ely EW. Delirium and cognitive dysfunction in the intensive care unit. Seminnars in respiratory and critical care medicine 2006;27(3):210‐20. [PUBMED: 16791755] - PubMed
Morandi 2008
-
- Morandi A, Phandharipande P, Trabucchi M, Rozzini R, Mistraletti G, Trompeo AC, et al. Understanding international differences in terminology for delirium and other types of acute brain dysfunction in critically ill patients. Intensive Care Medicine 2008;34(10):1907‐15. [PUBMED: 18563387] - PubMed
Morandi 2009
-
- Morandi A, Jackson JC, Ely EW. Delirium in the intensive care unit. International Review of Psychiatry 2009;21(1):43‐58. [PUBMED: 19219712] - PubMed
Morandi 2011
Nelson 2015
Neto 2012
-
- Neto AS, Nassar AP Jr, Cardoso SO, Manetta JA, Pereira VM, Espósito DC, et al. Delirium screening in critically ill patients: A systematic review and meta‐analysis. Critical Care Medicine 2012;40(6):1946‐51. [PUBMED: 22610196] - PubMed
Norman 2016
-
- Norman BC, Jackson JC, Graves JA, Girard TD, Pandharipande PP, Brummel NE, et al. Employment outcomes after critical illness: an analysis of the bringing to light the risk factors and incidence of neuropsychological dysfunction in ICU survivors cohort. Critical Care Medicine 2016;44(11):2003‐9. [PUBMED: 27171492 ] - PMC - PubMed
Oimet 2007
Oxenbøll‐Collet 2018
-
- Oxenbøll‐Collet M, Egerod I, Christensen V, Jensen J, Thomsen T. Nurses´ and physicians´ perceptions of Confusion Assessment Method for the intensive care unit for delirium detection: focus group study. Nursing in Critical Care 2018;23(1):16‐22. [PUBMED: 27596941] - PubMed
Pandharipande 2005
-
- Pandharipande P, Jackson J, Ely WE. Delirium: acute cognitive dysfunction in the critically ill. Current Opinion in Critical Care 2005;11(4):360‐8. [PUBMED: 16015117] - PubMed
Pandharipande 2008
Pandharipande 2010
Pandharipande 2013
Patel 2009
Peterson 2006
-
- Peterson JF, Pun BT, Dittus RS, Thomason JW, Jackson JC, Shintani AK, et al. Delirium and its motoric types: a study of 614 critically ill patients. Journal of the American Geriatric Society 2006;54(3):479‐84. [PUBMED: 16551316] - PubMed
Pfoh 2015
Pisani 2009
-
- Pisani MA, Kong SY, Kasl SV, Murphy TE, Araujo KLB, Ness PH. Days of delirium are associated with 1‐year mortality in an older intensive care unit population. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 2009;180(11):1092‐7. [DOI: 10.1164/rccm.200904-05370C; PUBMED: 19745202 ] - DOI - PMC - PubMed
RevMan 5.3 [Computer program]
-
- The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration. Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.3. Copenhagen: The Nordic Cochrane Centre, The Cochrane Collaboration, 2014.
Richter 2006
-
- Richter JC, Waydhas C, Pajonk FG. Incidence of posttraumatic stress disorder after prolonged surgical intensive care. Psycosomatics 2006;47(3):223‐30. [PUBMED: 16684939 ] - PubMed
Rose 2017
Rothenhaüsler 2001
-
- Rothenhaüsler HB, Ehrentraut S, Stoll C, Kampfammer HP. The relationship between cognitive performance and employment and health status in long‐term survivors of the acute respiratory distress syndrome : results of an exploratory study. General Hospital Psychiatry 2001;23(2):90‐6. [PUBMED: 11313077] - PubMed
Salluh 2009
-
- Salluh JIF, Dal‐Pizzol F, Mello PV, Friedman G, Silva E, Teles JM, et al. Delirium recognition and sedation practices in critically ill patients: A survey on the attitudes of 1015 Brazilian critical care physicians. Journal of Critical Care 2009;24(4):556‐62. [PUBMED: 19577412] - PubMed
Salluh 2015
Sanz 2009
-
- Sanz JC, Vargas ML, Marin JJ. Battery for assessment of neuropsychological status (RBANS) in schizophrenia: A pilot study in the Spanish population. Acta Neuropsychiatrica 2009;21(1):18‐25. [PUBMED: 25384525 ] - PubMed
Selim 2017
Serafim 2015
-
- Serafim RB, Bozza FA, Soares M, do Brasil PE, Tura BR, Ely EW. Pharmacologic prevention and treatment of delirium in intensive care patients: A systematic review. Journal of Critical Care 2015;30(4):799‐807. [PUBMED: 25957498] - PubMed
Shehabi 2010
-
- Shehabi Y, Riker RR, Bokesch BM, Wisemandle W, Shintani A, Ely EW. Delirium duration and mortality in lightly sedated, mechanically ventilated patients. Critical Care Medicine 2010;38(12):2311‐8. [PUBMED: 20838332] - PubMed
Shu‐Min Lin 2004
-
- Lin SM, Liu CY, Wang CH, Lin HC, Huang CD, Huang PY, et al. The impact of delirium on the survival of mechanically ventilated patients. Critical Care Medicine 2004;32(11):2254‐9. [PUBMED: 15640638 ] - PubMed
Siddiqi 2016
Strøm 2011
Svenningsen 2009
-
- Svenningsen H, Tønnesen E. Incidence of delirium in three Danish intensive care units. Ugeskrift for Læger 2009;171(49):3600‐4. [PUBMED: 19954700] - PubMed
Thomason 2005
Trogrlić 2015
van den Boogaard 2012a
-
- Boogaard M, Pickkers P, Slooter AJ, Kuiper MA, Spronk PE, Voort PH, et al. Development and validation of PRE‐DELIRIC ( PREdiction of DELIRium in ICUu patients ) delirium prediction model for intensive care patients : observational Multicentre study. BMJ 2012;344:e420. [PUBMED: 22323509 ] - PMC - PubMed
van den Boogaard 2012b
-
- Boogaard M, Schoonhoven L, Evers, AW, Hoeven JG, Achterberg T, Pickkers P. Delirium in critically ill patients: Impact on long‐term health‐related quality of life and cognitive functioning. Critical Care Medicine 2012;40(1):112‐8. [DOI: 10.1097/CCM.0B013e31822e99fc9; PUBMED: 21926597] - DOI - PubMed
van den Boogaard 2012c
-
- Boogaard M, Schoonhoven L, Hoeven JG, Achterberg T, Pickkers P. Incidence and short‐term consequences of delirium in critically ill patients : A prospective observational cohort study. International Journal of Nursing Studies 2012;49(7):775‐83. [PUBMED: 22197051] - PubMed
Vasilevskis 2010
Verceles 2012
-
- Verceles AC, Silhan L, Terrin M, Netzer G, Shanholtz C, Scharf SM. Circadian rhythm disruption in severe sepsis : the effect of ambient light on urinary 6‐sulfatoxymelatonin secretion. Intensive Care Medicine 2012;38(5):804‐10. [PUBMED: 22286671 ] - PubMed
Wan 2014
Wolters 2014
Woon 2012
-
- Woon FL, Dunn CB, Hopkins RO. Predicting cognitive sequelae in survivors of critical illness with cognitive screening tests. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care 2012;186(4):333‐40. [PUBMED: 22700858] - PubMed
Zaal 2015
-
- Zaal, IJ, Devlin JW, Hazelbag M, Klein Klowenberg PM, Kooi AW, Ong DS, et al. Benzodiazepine‐associated delirium in critically ill adults. Intensive Care Medicine Vol. 41, issue 12:2130‐7. [PUBMED: 26404392] - PubMed
References to other published versions of this review
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

