Porous Zero-Mode Waveguides for Picogram-Level DNA Capture
- PMID: 30484321
- PMCID: PMC9701543
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.8b04170
Porous Zero-Mode Waveguides for Picogram-Level DNA Capture
Abstract
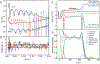
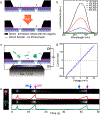
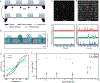
We have recently shown that nanopore zero-mode waveguides are effective tools for capturing picogram levels of long DNA fragments for single-molecule DNA sequencing. Despite these key advantages, the manufacturing of large arrays is not practical due to the need for serial nanopore fabrication. To overcome this challenge, we have developed an approach for the wafer-scale fabrication of waveguide arrays on low-cost porous membranes, which are deposited using molecular-layer deposition. The membrane at each waveguide base contains a network of serpentine pores that allows for efficient electrophoretic DNA capture at picogram levels while eliminating the need for prohibitive serial pore milling. Here, we show that the loading efficiency of these porous waveguides is up to 2 orders of magnitude greater than their nanopore predecessors. This new device facilitates the scaling-up of the process, greatly reducing the cost and effort of manufacturing. Furthermore, the porous zero-mode waveguides can be used for applications that benefit from low-input single-molecule real-time sequencing.
Keywords: Nanopore; SMRT sequencing; ZMWs; nanofabrication; porous membrane.
Figures
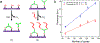
References
-
- Rothberg JM; Leamon JH Nat. Biotechnol 2008, 26, 1117–24. - PubMed
-
- Eid J; Fehr A; Gray J; Luong K; Lyle J; Otto G; Peluso P; Rank D; Baybayan P; Bettman B; Bibillo A; Bjornson K; Chaudhuri B; Christians F; Cicero R; Clark S; Dalal R; Dewinter A; Dixon J; Foquet M; Gaertner A; Hardenbol P; Heiner C; Hester K; Holden D; Kearns G; Kong X; Kuse R; Lacroix Y; Lin S; Lundquist P; Ma C; Marks P; Maxham M; Murphy D; Park I; Pham T; Phillips M; Roy J; Sebra R; Shen G; Sorenson J; Tomaney A; Travers K; Trulson M; Vieceli J; Wegener J; Wu D; Yang A; Zaccarin D; Zhao P; Zhong F; Korlach J; Turner S Science 2009, 323, 133–8. - PubMed
-
- Levy SE; Myers RM Annu. Rev. Genomics Hum. Genet 2016, 17, 95–115. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

