Altered expression of circular RNAs in human placental chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with hypoxia
- PMID: 30485544
- PMCID: PMC6818546
- DOI: 10.1002/jcla.22825
Altered expression of circular RNAs in human placental chorionic plate-derived mesenchymal stem cells pretreated with hypoxia
Abstract
Background: Hypoxic preconditioning alters the biological properties of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). It is not known whether this process has an effect on circular RNAs (circRNAs) in MSCs.
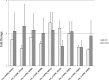
Methods: Human placental chorionic plate-derived MSCs (hpcpMSCs) isolated from the same placentae were classed into two groups: hypoxic pretreated (hypoxia) group and normally cultured (normoxia) group. The comparative circRNA microarray analysis was used to determine circRNAs expression and verified by quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in the two groups.
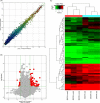
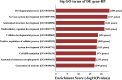
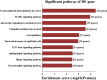
Results: One hundred and two differentially expressed circRNAs in the hypoxia group were found compared to that in the normoxia group (fold change >1.5-fold and P < 0.05). The expression levels of circRNAs by qRT-PCR were consistent with those evaluated by microarray analysis. Gene ontology (GO) analysis showed that the putative function of their target genes for those differentially expressed circRNAs was primarily involved in cell development and its differentiation and regulation. Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analysis revealed that transcriptional misregulation in cancer and mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) signaling pathway were the most significant. MAPK signaling pathway was found to be the core regulatory pathway triggered by hypoxia.
Conclusions: The results indicate that the altered expression of specific circRNAs in MSCs is associated with hypoxic preconditioning. This finding provides further exploration of underlying mechanisms of the characteristic changes of MSCs with hypoxic preconditioning.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Mohammadian M, Abasi E, Akbarzadeh A. Mesenchymal stem cell‐based gene therapy: a promising therapeutic strategy. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2016;44:1206‐1211. - PubMed
-
- Kim MJ, Shin KS, Jeon JH, et al. Human chorionic‐plate‐derived mesenchymal stem cells and Wharton's jelly‐derived mesenchymal stem cells: a comparative analysis of their potential as placenta‐derived stem cells. Cell Tissue Res. 2011;346:53‐64. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016A030310139/the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province
- 2015B050501003/the Southern China International Cooperation Base for Early Intervention and Functional Rehabilitation of Neurological Diseases
- 81601004/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- 81102248/the National Natural Science Foundation of China
- YIP-2016-014/Paediatric Institute Foundation of Guangzhou women and children's Medical Center
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

