Discovery and Characterization of Two Classes of Selective Inhibitors of the Suppressor of the TCR Signaling Family of Proteins
- PMID: 30485744
- PMCID: PMC6368478
- DOI: 10.1021/acsinfecdis.8b00238
Discovery and Characterization of Two Classes of Selective Inhibitors of the Suppressor of the TCR Signaling Family of Proteins
Abstract
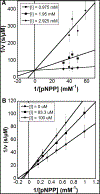
The suppressor of T-cell receptor signaling (Sts) proteins, Sts-1, has recently emerged as a potential immunostimulatory target for drug development. Genetic inactivation of the Sts proteins dramatically increases host survival of systemic infection and leads to improved pathogen clearance. The protein tyrosine phosphatase (PTP) activity of these proteins arises from a C-terminal 2-histidine phosphatase (HP) domain. To identify new inhibitors of the HP activity of Sts-1, we miniaturized a phosphatase assay to a 1536-well format and conducted a 20 580 compound screen. Among the hits were two classes of structurally related compounds, tetracycline variants and sulfonated azo dyes. These hits had low micromolar to nanomolar IC50 values. Orthogonal screening confirmed the validity of these inhibitors and demonstrated that both act competitively on Sts-1 phosphatase activity. When tested on other PTPs, PTP1B and SHP1, it was found that the tetracycline PTP1B, SHP1, the tetracycline variant (doxycycline), and the sulfonated azo dye (Congo red) are selective inhibitors of Sts-1HP, with selectivity indices ranging from 19 to as high as 200. The planar polyaromatic moieties present in both classes of compounds suggested a common binding mode. The mutation of either tryptophan 494 or tyrosine 596, located near the active site of the protein, reduced the Ki of the inhibitors from 3- to 18-fold, indicating that these residues may help to promote the binding of substrates with aromatic groups. This work provides new insights into substrate selectivity mechanisms and describes two classes of compounds that can serve as probes of function or as a basis for future drug discovery.
Keywords: PTP; Sts; TULA; UBASH3; tetracycline.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Insights into the suppressor of T-cell receptor (TCR) signaling-1 (Sts-1)-mediated regulation of TCR signaling through the use of novel substrate-trapping Sts-1 phosphatase variants.FEBS J. 2014 Feb;281(3):696-707. doi: 10.1111/febs.12615. Epub 2013 Dec 12. FEBS J. 2014. PMID: 24256567 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and Functional Characterization of the Histidine Phosphatase Domains of Human Sts-1 and Sts-2.Biochemistry. 2017 Sep 5;56(35):4637-4645. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.7b00638. Epub 2017 Aug 21. Biochemistry. 2017. PMID: 28759203 Free PMC article.
-
An unexpected 2-histidine phosphoesterase activity of suppressor of T-cell receptor signaling protein 1 contributes to the suppression of cell signaling.J Biol Chem. 2020 Jun 19;295(25):8514-8523. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA120.013482. Epub 2020 May 5. J Biol Chem. 2020. PMID: 32371395 Free PMC article.
-
The Sts Proteins: Modulators of Host Immunity.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 16;24(10):8834. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108834. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240179 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modulation of protein kinase signaling by protein phosphatases and inhibitors.Pharmacol Ther. 2002 Feb-Mar;93(2-3):307-17. doi: 10.1016/s0163-7258(02)00199-7. Pharmacol Ther. 2002. PMID: 12191622 Review.
Cited by
-
Roles of TULA-family proteins in T cells and autoimmune diseases.Genes Immun. 2025 Feb;26(1):54-62. doi: 10.1038/s41435-024-00300-8. Epub 2024 Nov 18. Genes Immun. 2025. PMID: 39558087 Review.
-
TULA Proteins in Men, Mice, Hens, and Lice: Welcome to the Family.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 23;24(11):9126. doi: 10.3390/ijms24119126. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37298079 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rebamipide and Derivatives are Potent, Selective Inhibitors of Histidine Phosphatase Activity of the Suppressor of T Cell Receptor Signaling Proteins.J Med Chem. 2024 Feb 8;67(3):1949-1960. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.3c01763. Epub 2024 Jan 22. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38252624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Singer AL, Koretzky GA. 2002. Control of T cell function by positive and negative regulators. Science 296:1639–40. - PubMed
-
- Carpino N, Turner S, Mekala D, Takahashi Y, Zang H, Geiger TL, Doherty P, Ihle JN. 2004. Regulation of ZAP-70 Activation and TCR Signaling by Two Related Proteins, Sts-1 and Sts-2. Immunity 20:37–46. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

