Cell Death in the Lung: The Apoptosis-Necroptosis Axis
- PMID: 30485762
- PMCID: PMC6598441
- DOI: 10.1146/annurev-physiol-020518-114320
Cell Death in the Lung: The Apoptosis-Necroptosis Axis
Abstract
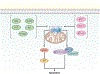
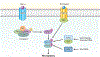
Regulated cell death is a major mechanism to eliminate damaged, infected, or superfluous cells. Previously, apoptosis was thought to be the only regulated cell death mechanism; however, new modalities of caspase-independent regulated cell death have been identified, including necroptosis, pyroptosis, and autophagic cell death. As an understanding of the cellular mechanisms that mediate regulated cell death continues to grow, there is increasing evidence that these pathways are implicated in the pathogenesis of many pulmonary disorders. This review summarizes our understanding of regulated cell death as it pertains to the pathogenesis of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, asthma, idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis, acute respiratory distress syndrome, and pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Keywords: acute respiratory distress syndrome; apoptosis; asthma; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease; idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; necroptosis; pulmonary arterial hypertension.
Figures
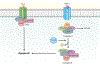

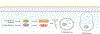
References
-
- Ashkenazi A, Salvesen G. 2014. Regulated cell death: signaling and mechanisms. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol 30:337–56 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

