Comparison of Salivary and Serum Soluble CD44 Levels between Patients with Oral SCC and Healthy Controls
- PMID: 30485941
- PMCID: PMC6318390
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.11.3059
Comparison of Salivary and Serum Soluble CD44 Levels between Patients with Oral SCC and Healthy Controls
Abstract
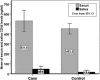
Background: The most common type of oral cancer is oral squamous cell carcinoma. If it is diagnosed in the early stages; the success of the treatment can be increased. It seems that ELISA-based techniques as a screening tool for society are the most cost-effective methods for early diagnosis. CD44 is a key marker for the detection of SCC stem cells. The aim of this study was to compare the level of soluble CD44 in saliva and serum between patients with oral SCC and healthy controls. Materials and Methods: Saliva and serum were collected from 20 patients with primary OSCC and 20 healthy persons as control group. The samples were evaluated by an ELISA test kit. Data were analyzed by SPSS software version 22, chi-square, ANOVA, T-test and Spearman correlation test. Results: The mean of soluble CD44 level in serum and saliva of the patient and control groups are 531.51±228.95 and 453.3±113.74 (for serum) and 48.53±59.02 and 17.76±39.14 (for saliva) respectively. There was no statistically significant difference in serum and saliva solCD44 level between the patient and control groups (P value = 0.182 and P value = 0.061 respectively). Also, there was no significant correlation between the solCD44 level in each patient and control group in serum (P value = 0.61) and in saliva (P value = 0.445). Conclusions: Determination of solCD44 level in saliva and serum can be a useful method for diagnosis the person’s involvement with cancer cells and the cancer in the early stages. But according to the controversial outcomes of past studies, larger and more accurate studies are needed in groups with more cases of oral cancer.
Keywords: CD44; oral squamous cell carcinoma; ELISA.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures
Similar articles
-
Salivary proteins from dysplastic leukoplakia and oral squamous cell carcinoma and their potential for early detection.J Proteomics. 2020 Feb 10;212:103574. doi: 10.1016/j.jprot.2019.103574. Epub 2019 Nov 7. J Proteomics. 2020. PMID: 31706945
-
CD44 and associated markers in oral rinses and tissues from oral and oropharyngeal cancer patients.Oral Oncol. 2020 Jul;106:104720. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2020.104720. Epub 2020 Apr 20. Oral Oncol. 2020. PMID: 32325304
-
Expression of p63 and CD44 in oral squamous cell carcinoma and correlation with clinicopathological parameters.Arch Oral Biol. 2017 Oct;82:160-165. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2017.06.011. Epub 2017 Jun 15. Arch Oral Biol. 2017. PMID: 28645102
-
Relevance of serum and salivary sialic acid in oral cancer diagnostics.J Cancer Res Ther. 2020 Apr-Jun;16(3):401-404. doi: 10.4103/jcrt.JCRT_512_19. J Cancer Res Ther. 2020. PMID: 32719243 Review.
-
The potential of CD44 as a diagnostic and prognostic tool in oral cancer.J Oral Pathol Med. 2015 Jul;44(6):393-400. doi: 10.1111/jop.12308. Epub 2015 Jan 30. J Oral Pathol Med. 2015. PMID: 25640063 Review.
Cited by
-
Predictive Value of Soluble PD-1, PD-L1, VEGFA, CD40 Ligand and CD44 for Nivolumab Therapy in Advanced Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Case-Control Study.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 18;12(2):473. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020473. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32085544 Free PMC article.
-
Biological biomarkers of oral cancer.Periodontol 2000. 2024 Oct;96(1):250-280. doi: 10.1111/prd.12542. Epub 2023 Dec 10. Periodontol 2000. 2024. PMID: 38073011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dynamic Measurement of a Cancer Biomarker: Towards In Situ Application of a Fiber-Optic Ball Resonator Biosensor in CD44 Protein Detection.Sensors (Basel). 2024 Mar 21;24(6):1991. doi: 10.3390/s24061991. Sensors (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38544254 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in the Diagnosis, Monitoring, and Progression of Oral Cancer through Saliva: An Update.Biomed Res Int. 2022 Oct 25;2022:2739869. doi: 10.1155/2022/2739869. eCollection 2022. Biomed Res Int. 2022. PMID: 36330456 Free PMC article.
-
Serum expression of Vascular Endothelial-Cadherin, CD44, Human High mobility group B1, Kallikrein 6 proteins in different stages of laryngeal intraepithelial lesions and early glottis cancer.PeerJ. 2022 Apr 19;10:e13104. doi: 10.7717/peerj.13104. eCollection 2022. PeerJ. 2022. PMID: 35462765 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allegra E, Trapasso S, Sacco A, et al. ELISA detection of salivary levels of Cd44sol as a diagnostic test for laryngeal carcinomas. J Cancer Sci Ther. 2012;4:330–4.
-
- Andratschke M, Chaubal S, Pauli C, et al. Soluble CD44v6 is not a sensitive tumor marker in patients with head and neck squamous cell cancer. Anticancer Res. 2005;25:2821–6. - PubMed
-
- Bonnet D, Dick JE. Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med. 1997;3:730–7. - PubMed
-
- Collins AT, Berry PA, Hyde C, Stower MJ, Maitland NJ. Prospective identification of tumorigenic prostate cancer stem cells. Cancer Res. 2005;65:10946–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous