Cognitive Deficits Following a Post-Myocardial Infarct in the Rat Are Blocked by the Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor Desvenlafaxine
- PMID: 30486235
- PMCID: PMC6320895
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19123748
Cognitive Deficits Following a Post-Myocardial Infarct in the Rat Are Blocked by the Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor Desvenlafaxine
Abstract
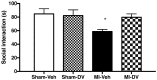
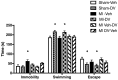
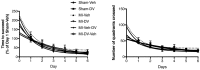
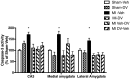
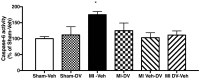
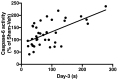
Myocardial infarction (MI) in animal models induces cognitive deficits as well as the activation of caspase in the limbic system; both can be blocked by 2 weeks of treatment following MI using tricyclic antidepressants or selective serotonin uptake blockers. Here we used three different treatment schedules to test the short- and long-term effects of the combined serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor desvenlafaxine on post-MI-associated cognitive deficits and caspase activation. MI was induced in 39 young adult rats, and 39 rats served as sham-operated controls. Desvenlafaxine (3 mg/kg/day, i.p.) or saline was administered according to one of three schedules: (1) for 2 weeks, starting right after surgery; (2) for 16 weeks, starting 2 weeks after surgery; (3) for 16 weeks, starting right after surgery. Behavior was tested 2 weeks (social interaction, passive avoidance) and 16 weeks (forced swimming, Morris water maze) after surgery. Caspase-3 and caspase-6 activities were measured 16 weeks after surgery. At 2 and 16 weeks post-surgery, saline-treated MI rats displayed performance deficits compared to desvenlafaxine-treated rats, regardless of the treatment schedule. Caspase-3 activity was higher in the amygdala (medial and lateral) and hippocampal CA3 region in untreated MI rats, whereas caspase-6 activity was higher in the CA1 region. Caspase-6 activity correlated positively with deficits in the Morris water maze. These results indicate that, independently of treatment schedules, various treatment schedules with desvenlafaxine can prevent MI-associated cognitive deficits and decrease caspase activities in the limbic system.
Keywords: behavior; caspase-3; caspase-6; desvenlafaxine; limbic system; memory; myocardial infarction.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
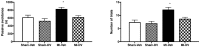

Similar articles
-
The effects of LPM570065, a novel triple reuptake inhibitor, on extracellular serotonin, dopamine and norepinephrine levels in rats.PLoS One. 2014 Mar 10;9(3):e91775. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091775. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24614602 Free PMC article.
-
Desvenlafaxine reduces apoptosis in amygdala after myocardial infarction.Brain Res Bull. 2014 Oct;109:158-63. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2014.10.012. Epub 2014 Nov 6. Brain Res Bull. 2014. PMID: 25451696
-
Vulnerability for apoptosis in the limbic system after myocardial infarction in rats: a possible model for human postinfarct major depression.J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2007 Jan;32(1):11-6. J Psychiatry Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17245469 Free PMC article.
-
[Desvenlafaxine and neuropathic pain: additional clinical benefits of a second generation serotonin-noradrenaline reuptake inhibitor].Rev Neurol. 2017 Mar 1;64(5):219-226. Rev Neurol. 2017. PMID: 28229443 Review. Spanish.
-
Desvenlafaxine for major depressive disorder: incremental clinical benefits from a second-generation serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor.Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010 Dec;6(12):1565-74. doi: 10.1517/17425255.2010.535810. Epub 2010 Nov 11. Expert Opin Drug Metab Toxicol. 2010. PMID: 21067460 Review.
Cited by
-
The impact of myocardial infarction on basal and stress-induced heart rate variability and cortisol secretion in women: A pilot study.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2022 Jan 13;9:100113. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2022.100113. eCollection 2022 Feb. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2022. PMID: 35755922 Free PMC article.
-
Bifidobacterium longum R0175 attenuates post-myocardial infarction depressive-like behaviour in rats.PLoS One. 2019 Apr 22;14(4):e0215101. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0215101. eCollection 2019. PLoS One. 2019. PMID: 31009477 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deckers K., Schievink S.H.J., Rodriquez M.M.F., van Oostenbrugge R.J., van Boxtel M.P.J., Verhey F.R.J., Kohler S. Coronary heart disease and risk for cognitive impairment or dementia: Systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0184244. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0184244. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Wann B.P., Bah T.M., Kaloustian S., Boucher M., Dufort A.M., Le Marec N., Godbout R., Rousseau G. Behavioural signs of depression and apoptosis in the limbic system following myocardial infarction: Effects of sertraline. J. Psychopharmacol. 2009;23:451–459. doi: 10.1177/0269881108089820. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Bah T.M., Benderdour M., Kaloustian S., Karam R., Rousseau G., Godbout R. Escitalopram reduces circulating pro-inflammatory cytokines and improves depressive behavior without affecting sleep in a rat model of post-cardiac infarct depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2011;225:243–251. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2011.07.039. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

