Pterostilbene Attenuates Hexavalent Chromium-Induced Allergic Contact Dermatitis by Preventing Cell Apoptosis and Inhibiting IL-1β-Related NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
- PMID: 30486377
- PMCID: PMC6306791
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm7120489
Pterostilbene Attenuates Hexavalent Chromium-Induced Allergic Contact Dermatitis by Preventing Cell Apoptosis and Inhibiting IL-1β-Related NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation
Abstract
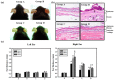
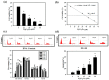
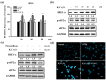
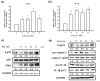
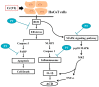
Hexavalent chromium (Cr(VI)) is widely used in many industries but can induce contact dermatitis especially in cement industries. Many cement workers suffer from Cr(VI)-induced allergic contact dermatitis (ACD), and prevention and therapeutic strategies are still lacking. Pterostilbene (PT) is a natural compound predominantly found in blueberries. Studies indicate the potential use of PT as an effective anti-oxidative and anti-inflammatory agent. Herein, we investigated the possible mechanisms involved and whether chromium-induced ACD could be effectively inhibited by treating PT. In our in vivo study, epidermal Cr(VI) administration causes cutaneous inflammation in mice ear skin, and the pro-inflammatory cytokines, TNF-α and IL-1β, were found in the epidermis, presenting the level of increase after Cr(VI) treatment. Meanwhile, the results of our in vitro experiment showed that apoptosis and endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress were induced after treatment with different concentrations of Cr(VI) in HaCaT cells (human keratinocyte). Cr(VI) also induced TNF-α and IL-1β mRNA expressions, through the activation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK)/MAPK-activated protein kinase 2 (MK2) pathway. Notably, the severity of the skin reactions in the epicutaneous elicitation test significantly diminished when the mouse was treated with PT. Likewise, PT intervention also ameliorated the inflammation and apoptosis of HaCaT cells in vitro. Furthermore, our current findings demonstrated that the NLRP3 inflammasome could be involved in the Cr(VI)-mediated inflammation and apoptosis of ACD. Thus, interrupting this mechanism with proper nontoxic agents, such as PT, could be a new option to improve occupational chromium toxicity and hypersensitivity.
Keywords: NLRP3 inflammasome; allergic contact dermatitis; endoplasmic reticulum stress; hexavalent chromium; inflammatory cytokines; pterostilbene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Skin application of glutathione and iron sulfate can inhibit elicitation of allergic contact dermatitis from hexavalent chromium.Contact Dermatitis. 2020 Jan;82(1):45-53. doi: 10.1111/cod.13409. Epub 2019 Nov 14. Contact Dermatitis. 2020. PMID: 31584201 Clinical Trial.
-
N-acetylcysteine attenuates hexavalent chromium-induced hypersensitivity through inhibition of cell death, ROS-related signaling and cytokine expression.PLoS One. 2014 Sep 23;9(9):e108317. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0108317. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 25248126 Free PMC article.
-
A retrospective investigation of hexavalent chromium allergy in southern Sweden.Contact Dermatitis. 2018 Jun;78(6):386-392. doi: 10.1111/cod.12969. Epub 2018 Mar 23. Contact Dermatitis. 2018. PMID: 29572843
-
Review of the allergic contact dermatitis hazard posed by chromium-contaminated soil: identifying a "safe" concentration.J Toxicol Environ Health. 1992 Sep;37(1):177-207. doi: 10.1080/15287399209531664. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1992. PMID: 1522610 Review.
-
Risk assessment of the allergic dermatitis potential of environmental exposure to hexavalent chromium.J Toxicol Environ Health. 1993 Dec;40(4):613-41. doi: 10.1080/15287399309531822. J Toxicol Environ Health. 1993. PMID: 8277522 Review.
Cited by
-
IL-1β and Allergy: Focusing on Its Role in Allergic Rhinitis.Mediators Inflamm. 2023 Apr 12;2023:1265449. doi: 10.1155/2023/1265449. eCollection 2023. Mediators Inflamm. 2023. PMID: 37091903 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Overview of Hexavalent Chromium-Induced Necroptosis, Pyroptosis, and Ferroptosis.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025 May;203(5):2619-2635. doi: 10.1007/s12011-024-04376-1. Epub 2024 Sep 17. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2025. PMID: 39287767 Review.
-
The Potential of Polyphenols in Modulating the Cellular Senescence Process: Implications and Mechanism of Action.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 22;18(2):138. doi: 10.3390/ph18020138. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40005954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Inhibition of UVB radiation-induced tissue swelling and immune suppression by nicotinamide riboside and pterostilbene.Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2024 May;40(3):e12961. doi: 10.1111/phpp.12961. Photodermatol Photoimmunol Photomed. 2024. PMID: 38676310 Free PMC article.
-
The bioactivities of resveratrol and its naturally occurring derivatives on skin.J Food Drug Anal. 2021 Mar 15;29(1):15-38. doi: 10.38212/2224-6614.1151. J Food Drug Anal. 2021. PMID: 35696226 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Toncic R.J., Lipozencic J., Martinac I., Greguric S. Immunology of allergic contact dermatitis. Acta Dermatovenerol. Croat. 2011;19:51–68. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

