Exploiting the Electronic Tuneability of Carboranes as Supports for Frustrated Lewis Pairs
- PMID: 30486434
- PMCID: PMC6321043
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23123099
Exploiting the Electronic Tuneability of Carboranes as Supports for Frustrated Lewis Pairs
Abstract
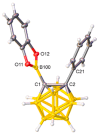
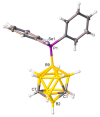
The first example of a carborane with a catecholborolyl substituent, [1-Bcat-2-Ph-closo-1,2-C₂B10H10] (1), has been prepared and characterized and shown to act as the Lewis acid component of an intermolecular frustrated Lewis pair in catalyzing a Michael addition. In combination with B(C₆F₅)₃ the C-carboranylphosphine [1-PPh₂-closo-1,2-C₂B10H11] (IVa) is found to be comparable with PPh₂(C₆F₅) in its ability to catalyze hydrosilylation, whilst the more strongly basic B-carboranylphosphine [9-PPh₂-closo-1,7-C₂B10H11] (V) is less effective and the very weakly basic species [μ-2,2'-PPh-{1-(1'-1',2'-closo-C₂B10H10)-1,2-closo-C₂B10H10}] (IX) is completely ineffective. Base strengths are rank-ordered via measurement of the ¹J 31P-77Se coupling constants of the phosphineselenides [1-SePPh₂-closo-1,2-C₂B10H11] (2), [9-SePPh₂-closo-1,7-C₂B10H11] (3), and [SePPh₂(C₆F₅)] (4).
Keywords: carborane; catalysis; frustrated Lewis pair; phosphine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
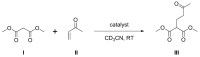




Similar articles
-
On the Basicity of Carboranylphosphines.Inorg Chem. 2019 Nov 4;58(21):14818-14829. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.9b02486. Epub 2019 Oct 22. Inorg Chem. 2019. PMID: 31638782
-
Large, weakly basic bis(carboranyl)phosphines: an experimental and computational study.Dalton Trans. 2017 Apr 19;46(16):5218-5228. doi: 10.1039/c7dt00485k. Dalton Trans. 2017. PMID: 28378864
-
Silver-phosphine complexes of the highly methylated carborane monoanion [closo-1-H-CB11Me11]-.J Am Chem Soc. 2004 Feb 11;126(5):1503-17. doi: 10.1021/ja038173m. J Am Chem Soc. 2004. PMID: 14759209
-
[Reaction Development on π- and σ-Conjugated Bonds and Creation of Innovative Functions].Yakugaku Zasshi. 2016;136(6):883-93. doi: 10.1248/yakushi.15-00294. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2016. PMID: 27252066 Review. Japanese.
-
Transition metal-carboryne complexes: synthesis, bonding, and reactivity.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Apr 19;44(4):299-309. doi: 10.1021/ar100156f. Epub 2011 Mar 11. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21395260 Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Reactivity of B-Connected Carboranylphosphines in Frustrated Lewis Pair Chemistry: A New Frame for a Classic System.Chemistry. 2022 Jun 15;28(34):e202200531. doi: 10.1002/chem.202200531. Epub 2022 May 12. Chemistry. 2022. PMID: 35472172 Free PMC article.
-
Crystal structure of 1-hepta-fluoro-tolyl-closo-1,2-dicarbadodeca-borane.Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2019 Mar 29;75(Pt 4):512-515. doi: 10.1107/S2056989019004067. eCollection 2019 Apr 1. Acta Crystallogr E Crystallogr Commun. 2019. PMID: 31161066 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

