Two Novel Multi-Functional Peptides from Meat and Visceral Mass of Marine Snail Neptunea arthritica cumingii and Their Activities In Vitro and In Vivo
- PMID: 30486436
- PMCID: PMC6315844
- DOI: 10.3390/md16120473
Two Novel Multi-Functional Peptides from Meat and Visceral Mass of Marine Snail Neptunea arthritica cumingii and Their Activities In Vitro and In Vivo
Abstract
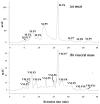
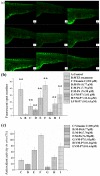
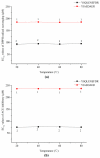
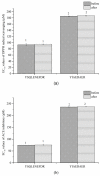
Neptunea arthritica cumingii (Nac) is a marine snail with high nutritional and commercial value; however, little is known about its active peptides. In this study, two multi-functional peptides, YSQLENEFDR (Tyr-Ser-Gln-Leu-Glu-Asn-Glu-Phe-Asp-Arg) and YIAEDAER (Tyr-Ile-Ala-Glu-Asp-Ala-Glu-Arg), were isolated and purified from meat and visceral mass extracts of Nac using a multi-bioassay-guided method and were characterized by using liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry. Both peptides showed high antioxidant, angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE)-inhibitory, and anti-diabetic activities, with half-maximal effective concentrations values less than 1 mM. Antioxidant and ACE-inhibitory activities were significantly higher for YSQLENEFDR than for YIAEDAER. In a zebrafish model, the two peptides exhibited strong scavenging ability for reactive oxygen species and effectively protected skin cells against oxidative damage without toxicity. Molecular docking simulation further predicted the interactions of the two peptides and ACE. Stability analysis study indicated that the two synthetic peptides maintained their activities under thermal stress and simulated gastrointestinal digestion conditions. The low molecular weight, high proportion of hydrophobic and negatively-charged amino acids, and specific C-terminal and N-terminal amino acids may contribute to the observed bio-activities of these two peptides with potential application for the prevention of chronic noncommunicable diseases.
Keywords: ACE-inhibitory activity; Neptunea arthritica cumingii; anti-diabetic activity; antioxidant activity; multi-functional peptides.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

