Cloning, Characterization and Anion Inhibition Studies of a β-Carbonic Anhydrase from the Pathogenic Protozoan Entamoeba histolytica
- PMID: 30486513
- PMCID: PMC6321543
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules23123112
Cloning, Characterization and Anion Inhibition Studies of a β-Carbonic Anhydrase from the Pathogenic Protozoan Entamoeba histolytica
Abstract
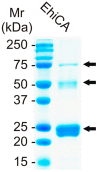
We report the cloning and catalytic activity of a β-carbonic anhydrase (CA, EC 4.2.1.1), isolated from the pathogenic protozoan Entamoeba histolytica, EhiCA. This enzyme has a high catalytic activity for the physiologic CO₂ hydration reaction, with a kcat of 6.7 × 10⁵ s-1 and a kcat/Km of 8.9 × 10⁷ M-1 × s-1. An anion inhibition study of EhiCA with inorganic/organic anions and small molecules revealed that fluoride, chloride, cyanide, azide, pyrodiphosphate, perchlorate, tetrafluoroborate and sulfamic acid did not inhibit the enzyme activity, whereas pseudohalides (cyanate and thiocyanate), bicarbonate, nitrate, nitrite, diethyldithiocarbamate, and many complex inorganic anions showed inhibition in the millimolar range (KIs of 0.51⁻8.4 mM). The best EhiCA inhibitors were fluorosulfonate, sulfamide, phenylboronic acid and phenylarsonic acid (KIs in the range of 28⁻86 μM). Since β-CAs are not present in vertebrates, the present study may be useful for detecting lead compounds for the design of effective enzyme inhibitors, with potential to develop anti-infectives with alternative mechanisms of action.
Keywords: Entamoeba histolytica; anions; carbonic anhydrase; inhibitor; metalloenzymes; protozoan.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors do not declare conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sulfonamide Inhibition Studies of a New β-Carbonic Anhydrase from the Pathogenic Protozoan Entamoeba histolytica.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Dec 8;19(12):3946. doi: 10.3390/ijms19123946. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30544802 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, characterization and anion inhibition studies of a new γ-carbonic anhydrase from the Antarctic bacterium Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis.Bioorg Med Chem. 2015 Aug 1;23(15):4405-4409. doi: 10.1016/j.bmc.2015.06.021. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Bioorg Med Chem. 2015. PMID: 26145820
-
Cloning, characterization and anion inhibition studies of a γ-carbonic anhydrase from the Antarctic cyanobacterium Nostoc commune.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Nov 1;25(21):4970-4975. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.03.010. Epub 2015 Mar 11. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 25804721
-
Legionella pneumophila Carbonic Anhydrases: Underexplored Antibacterial Drug Targets.Pathogens. 2016 Jun 16;5(2):44. doi: 10.3390/pathogens5020044. Pathogens. 2016. PMID: 27322334 Free PMC article. Review.
-
(In)organic anions as carbonic anhydrase inhibitors.J Inorg Biochem. 2012 Jun;111:117-29. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2011.11.017. Epub 2011 Dec 1. J Inorg Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22192857 Review.
Cited by
-
Activation Studies of the γ-Carbonic Anhydrases from the Antarctic Marine Bacteria Pseudoalteromonas haloplanktis and Colwellia psychrerythraea with Amino Acids and Amines.Mar Drugs. 2019 Apr 22;17(4):238. doi: 10.3390/md17040238. Mar Drugs. 2019. PMID: 31013612 Free PMC article.
-
Cloning, characterization, and inhibition of the novel β-carbonic anhydrase from parasitic blood fluke, Schistosoma mansoni.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023 Dec;38(1):2184299. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2023.2184299. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36856011 Free PMC article.
-
Activation Studies of the β-Carbonic Anhydrase from the Pathogenic Protozoan Entamoeba histolytica with Amino Acids and Amines.Metabolites. 2019 Feb 1;9(2):26. doi: 10.3390/metabo9020026. Metabolites. 2019. PMID: 30717275 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical and structural characterisation of a protozoan beta-carbonic anhydrase from Trichomonas vaginalis.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020 Dec;35(1):1292-1299. doi: 10.1080/14756366.2020.1774572. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2020. PMID: 32515610 Free PMC article.
-
Novel 2,4-Dichloro-5-sulfamoylbenzoic Acid Oxime Esters: First Studies as Potential Human Carbonic Anhydrase Inhibitors.ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024 May 23;15(6):972-978. doi: 10.1021/acsmedchemlett.4c00206. eCollection 2024 Jun 13. ACS Med Chem Lett. 2024. PMID: 38894925 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Vullo D., Del Prete S., Di Fonzo P., Carginale V., Donald W.A., Supuran C.T., Capasso C. Comparison of the sulfonamide inhibition profiles of the β- and γ-carbonic anhydrases from the pathogenic bacterium Burkholderia pseudomallei. Molecules. 2017;22:421. doi: 10.3390/molecules22030421. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

