Ki-67 Prognostic Value in Different Histological Grades of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- PMID: 30486632
- PMCID: PMC6318382
- DOI: 10.31557/APJCP.2018.19.11.3279
Ki-67 Prognostic Value in Different Histological Grades of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Abstract
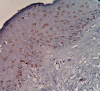
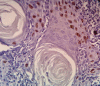
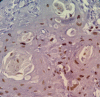
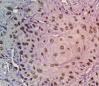
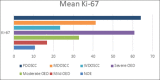
Introduction: Abnormal cell proliferation appears to be a possible predictor of tumorigenesis, Ki-67 protein expression is closely related to the cell proliferation and could be used as a biomarker for the growth in the most of human tumors. The aim of the study: Investigating of Ki-67 expression in the pathological grades of oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinomas. Materials and Methods: The sample consisted of 30 formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded specimens of oral epithelial dysplasia (OED), 30 other of oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC), and 10 normal oral epithelium (NOE) were conventionally stained with hematoxylin and eosin and immunohistochemically stained with Ki-67 monoclonal antibody. Results: Expression of Ki-67 was restricted to the basal layers in the normal oral epithelium whereas Ki-67 positive cells in oral epithelial dysplasia (OED) were located in the basal, suprabasal and spinous layers, Ki-67 expression was increased in high-risk cases. Ki-67 positive cells in well-differentiated (OSCC) were located mainly in the periphery of the tumor nests, in moderately-differentiated (OSCC) were located in both peripheral and part of a center of the tumor nests whereas it was diffused in most of the Poorly-differentiated (OSCC). Statistical analysis indicated a significant difference between the expression in (OED) and (NOE), (OSCC) and (NOE), and no differences between (OED) and (OSCC). Conclusion: This study has concluded that Ki-67 antigen could be used as a marker for the histological grading of OED and OSCC, Expression of Ki 67 increased according to the severity of oral epithelial dysplasia.
Keywords: Ki-67 antigen; Oral epithelial dysplasia (OED); Oral squamous cell carcinomas (OSCC); NOE.
Creative Commons Attribution License
Figures



Similar articles
-
Immunohistochemical Evaluation of GLUT-3 and GLUT-4 in Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018 Jul 27;19(7):1779-1783. doi: 10.22034/APJCP.2018.19.7.1779. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2018. PMID: 30049187 Free PMC article.
-
A comparative analysis of langerhans cell in oral epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma using antibody CD-1a.J Cancer Res Ther. 2012 Oct-Dec;8(4):591-7. doi: 10.4103/0973-1482.106565. J Cancer Res Ther. 2012. PMID: 23361280
-
Ki-67 Expression as a Prognostic Marker: A Comparative Immunohistochemical Analysis of Oral Epithelial Dysplasia and Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cureus. 2023 May 12;15(5):e38941. doi: 10.7759/cureus.38941. eCollection 2023 May. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37313057 Free PMC article.
-
An Update on the Use of Artificial Intelligence in Digital Pathology for Oral Epithelial Dysplasia Research.Head Neck Pathol. 2024 May 10;18(1):38. doi: 10.1007/s12105-024-01643-4. Head Neck Pathol. 2024. PMID: 38727841 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The promise of stem cell markers in the diagnosis and therapy of epithelial dysplasia and oral squamous cell carcinoma.J Cell Physiol. 2018 Nov;233(11):8499-8507. doi: 10.1002/jcp.26789. Epub 2018 May 24. J Cell Physiol. 2018. PMID: 29797575 Review.
Cited by
-
Poor Prognosis of Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Correlates With ITGA6.Int Dent J. 2023 Apr;73(2):178-185. doi: 10.1016/j.identj.2022.05.010. Epub 2022 Jul 9. Int Dent J. 2023. PMID: 35820930 Free PMC article.
-
Deep learning for the standardized classification of Ki-67 in vulva carcinoma: A feasibility study.Heliyon. 2021 Jul 15;7(7):e07577. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07577. eCollection 2021 Jul. Heliyon. 2021. PMID: 34386617 Free PMC article.
-
An Immunohistochemical Study Showing Ki-67 as an Analytical Marker in Oral Malignant and Premalignant Lesions.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2020 Aug;12(Suppl 1):S274-S278. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.JPBS_83_20. Epub 2020 Aug 28. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2020. PMID: 33149470 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing Cervical Cancer Screening: Review of p16/Ki-67 Dual Staining as a Promising Triage Strategy.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Feb 19;14(4):451. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14040451. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38396493 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential Expression of EZH2 and H3K27me3 in Oral Verrucous Carcinoma and Oral Verrucous Hyperplasia.Head Neck Pathol. 2021 Jun;15(2):408-415. doi: 10.1007/s12105-020-01209-0. Epub 2020 Jul 27. Head Neck Pathol. 2021. PMID: 32720035 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bacchi C, Gown A. Detection of cell proliferation in tissue sections. Braz J Med Biol Res. 1993;26:677–87. - PubMed
-
- Boeve K, Schepman KP, Schuuring E, et al. High sensitivity and negative predictive value of sentinel lymph node biopsy in a retrospective early stage oral cavity cancer cohort in the Northern Netherlands. Clin Otolaryngol. 2018;18:89. - PubMed
-
- Booth DG, Earnshaw WC. Ki-67 and the chromosome periphery compartment in mitosis. Trends Cell Biol. 2017;5:458. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

