The training contents, problems and needs of doctors in urban community health service institutions in China
- PMID: 30486771
- PMCID: PMC6263560
- DOI: 10.1186/s12875-018-0867-6
The training contents, problems and needs of doctors in urban community health service institutions in China
Abstract
Background: The Chinese government offered various types of training programs for strengthening the role of doctors working in community health service institutions (CHSIs). The study intended to investigate the current training programs and training needs of doctors nationally in urban CHSIs in China, and to provide propositions for training more qualified doctors in the future.
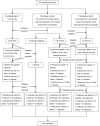
Methods: Total 3098 doctors in 192 urban CHSIs were chosen from 9 provinces (Hebei, Liaoning, Shandong, Zhejiang, Fujian, Hunan, Guangxi, Guizhou, Ningxia) and one municipality (Beijing) among 31 provinces in eastern, central, and western regions by stratified sampling methods in Mainland China. All doctors in the selected CHSIs were investigated in this study. We discharged 3073 questionnaires, and the response rate was 98.0%. Descriptive statistics were used to describe the characteristics, training contents, problems and needs of doctors. Differences in training contents, problems and needs between eastern, central and western regions were analyzed with chi-square tests.
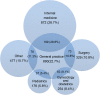
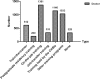
Results: 49.3% of doctors in CHSIs had Bachelor's degree and beyond. 12.9% of doctors had senior professional titles. The most frequent training topics for the doctors in eastern, central and western regions were "basic clinical theory knowledge" (52.4%), "community health service competency" (59.6%), "clinical practice skills" (45.9%) respectively. The most serious problem for doctors was "insufficient training time" in eastern (36.8%), central (36.5%) and western (39.6%). The biggest knowledge need for doctors both in eastern (79.8%) and central region (79.1%) was "the updated international medical knowledge", in western region it was "the updated domestic medical knowledge" (73.2%). The biggest skill-related training need for doctors in eastern region (84.1%) and central region (82.6%) was "communication skills", and "diagnosis and differential diagnosis" in western region (78.2%).
Conclusion: Government should design proper training contents according to the knowledge and skill needs of different design. Furthermore, a uniform, rigorous training and evaluation system focus on practicability should be established to promote community health service system in Mainland China.
Keywords: Doctors; Training needs; Training programs; Urban community health care service institutions.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
It was approved by the Ethical Committee of Capital Medical University, Beijing, China. Data were obtained from a 2011 cross-sectional survey, the Nationwide Investigation on Health Professionals of Community Health Service Institutions in Urban China. Written informed consent was obtained from each participant involved in this study.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China. China health statistical yearbook 2013 [in Chinese]; 2013. Available from: http://www.nhfpc.gov.cn/htmlfiles/zwgkzt/ptjnj/year2013/index2013.html. Accessed 26 Apr 2014.
-
- National Health and Family Planning Commission of the People’s Republic of China [Internet] The notice of medicine and health care medium-term and long-term talents development plan (2011–2020) issued by Ministry of Health [in Chinese] 2011.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

