Growth zone segmentation in the milkweed bug Oncopeltus fasciatus sheds light on the evolution of insect segmentation
- PMID: 30486779
- PMCID: PMC6262967
- DOI: 10.1186/s12862-018-1293-z
Growth zone segmentation in the milkweed bug Oncopeltus fasciatus sheds light on the evolution of insect segmentation
Abstract
Background: One of the best studied developmental processes is the Drosophila segmentation cascade. However, this cascade is generally considered to be highly derived and unusual, with segments being patterned simultaneously, rather than the ancestral sequential segmentation mode. We present a detailed analysis of the segmentation cascade of the milkweed bug Oncopletus fasciatus, an insect with a more primitive segmentation mode, as a comparison to Drosophila, with the aim of reconstructing the evolution of insect segmentation modes.
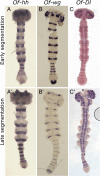
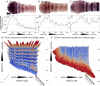
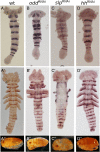
Results: We document the expression of 12 genes, representing different phases in the segmentation process. Using double staining we reconstruct the spatio-temporal relationships among these genes. We then show knock-down phenotypes of representative genes in order to uncover their roles and position in the cascade.
Conclusions: We conclude that sequential segmentation in the Oncopeltus germband includes three slightly overlapping phases: Primary pair-rule genes generate the first segmental gene expression in the anterior growth zone. This pattern is carried anteriorly by a series of secondary pair-rule genes, expressed in the transition between the growth zone and the segmented germband. Segment polarity genes are expressed in the segmented germband with conserved relationships. Unlike most holometabolous insects, this process generates a single-segment periodicity, and does not have a double-segment pattern at any stage. We suggest that the evolutionary transition to double-segment patterning lies in mutually exclusive expression patterns of secondary pair-rule genes. The fact that many aspects of the putative Oncopeltus segmentation network are similar to those of Drosophila, is consistent with a simple transition between sequential and simultaneous segmentation.
Keywords: Arthropod; Body plan; Evo-devo; Segment.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All work reported herein was on invertebrate animals that do not require ethical approval.
Consent for publication
N/A
Competing interests
The authors declare they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures




References
-
- Lawrence PA. The making of a fly: the genetics of animal design. Oxford: Blackwell Scientific Publications; 1992.
-
- Hartenstein V, Chipman AD. Hexapoda: a Drosophila’s view of insect development. In: Wanninger A, editor. Evolutionary Developmental Biology of Invertebrates. Vienna: Springer; 2015. pp. 1–91.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

