Prevalence of and risk factors for fatty liver in the general population of Northern Italy: the Bagnacavallo Study
- PMID: 30486798
- PMCID: PMC6262973
- DOI: 10.1186/s12876-018-0906-8
Prevalence of and risk factors for fatty liver in the general population of Northern Italy: the Bagnacavallo Study
Abstract
Background: The estimation of the burden of disease attributable to fatty liver requires studies performed in the general population.
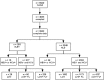
Methods: The Bagnacavallo Study was performed between October 2005 and March 2009. All the citizens of Bagnacavallo (Ravenna, Italy) aged 30 to 60 years as of January 2005 were eligible. Altered liver enzymes were defined as alanine transaminase > 40 U/l and/or aspartate transaminase > 37 U/l.
Results: Four thousand and thirty-three (58%) out of 6920 eligible citizens agreed to participate and 3933 (98%) had complete data. 393 (10%) of the latter had altered liver enzymes and 3540 had not. After exclusion of subjects with HBV or HCV infection, liver ultrasonography was available for 93% of subjects with altered liber enzymes and 52% of those with normal liver enzymes. The prevalence of fatty liver, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic fatty liver disease (AFLD) was 0.74 (95%CI 0.70 to 0.79) vs. 0.35 (0.33 to 0.37), 0.46 (0.41 to 0.51) vs. 0.22 (0.21 to 0.24) and 0.28 (0.24 to 0.33) vs. 0.13 (0.11 to 0.14) in citizens with than in those without altered liver enzymes. Ethanol intake was not associated and all the components of the metabolic syndrome (MS) were associated with fatty liver. All potential risk factors were associated with a lower odds of normal liver vs. NAFLD while they were unable to discriminate AFLD from NAFLD.
Conclusions: Fatty liver as a whole was highly prevalent in Bagnacavallo in 2005/9 and was more common among citizens with altered liver enzymes.
Keywords: chronic liver disease; cross-sectional study; epidemiology; fatty liver; prevalence; risk factors.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study was approved by the Ethical Committee of Area Vasta Romagna - IRST (reference number 112). All citizens gave written informed consent.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Stefano Bellantani is an Editorial Board Member for BMC Gastroenterology.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures

References
-
- EASL-EASD-EASO EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J Hepatol. 2016;64:1388–1402. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

