Controlled trial of the impact of a BC adult mental health practice support program (AMHPSP) on primary health care professionals' management of depression
- PMID: 30486799
- PMCID: PMC6262957
- DOI: 10.1186/s12875-018-0862-y
Controlled trial of the impact of a BC adult mental health practice support program (AMHPSP) on primary health care professionals' management of depression
Abstract
Background: Depression affects over 400 million people globally. The majority are seen in primary care. Barriers in providing adequate care are not solely related to physicians' knowledge/skills deficits, but also time constraints, lack of confidence/avoidance, which need to be addressed in mental health-care redesign. We hypothesized that family physician (FP) training in the Adult Mental Health Practice Support Program (AMHPSP) would lead to greater improvements in patient depressive symptom ratings (a priori primary outcome) compared to treatment as usual.
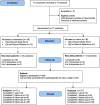
Methods: From October 2013 to May 2015, in a controlled trial 77 FP practices were stratified on the total number of physicians/practice as well as urban/rural setting, and randomized to the British Columbia AMHPSP⎯a multi-component contact-based training to enhance FPs' comfort/skills in treating mild-moderate depression (intervention), or no training (control) by an investigator not operationally involved in the trial. FPs with a valid license to practice in NS were eligible. FPs from both groups were asked to identify 3-4 consecutive patients > 18 years old, diagnosis of depression, Patient Health Questionnaire (PHQ-9) score ≥ 10, able to read English, intact cognitive functioning.
Exclusion criteria: antidepressants within 5 weeks and psychotherapy within 3 months of enrollment, and clinically judged urgent/emergent medical/psychiatric condition. Patients were assigned to the same arm as their physician. Thirty-six practices recruited patients (intervention n = 23; control n = 13). The study was prematurely terminated at 6 months of enrollment start-date due to concomitant primary health-care transformation by health-system leaders which resulted in increased in-office demands, and recruitment failure. We used the PHQ-9 to assess between-group differences at baseline, 1, 2, 3, and 6 months follow-up. Outcome collectors and assessors were blind to group assignment.
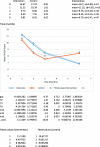
Results: One hundred-and-twenty-nine patients (intervention n = 72; control n = 57) were analysed. A significant improvement in depression scores among intervention group patients emerged between 3 and 6 months, time by treatment interaction, likelihood ratio test (LR) chi2(3) = 7.96, p = .047.
Conclusions: This novel skill-based program shows promise in translating increased FP comfort and skills managing depressed patients into improved patient clinical outcomes⎯even in absence of mental health specialists availability.
Trial registration: #NCT01975948 .
Keywords: Depressive disorders; Mental disorders; Patient-centered outcomes; Primary care; Skill-based training.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The Nova Scotia Multisite and University of Calgary Research Ethics Boards approved this study, registration
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Family physicians' involvement and self-reported comfort and skill in care of children with behavioral and emotional problems: a population-based survey.BMC Fam Pract. 2005 Mar 11;6(1):12. doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-6-12. BMC Fam Pract. 2005. PMID: 15762982 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of a quality improvement intervention for adolescent depression in primary care clinics: a randomized controlled trial.JAMA. 2005 Jan 19;293(3):311-9. doi: 10.1001/jama.293.3.311. JAMA. 2005. PMID: 15657324 Clinical Trial.
-
Impact of Skill-Based Approaches in Reducing Stigma in Primary Care Physicians: Results from a Double-Blind, Parallel-Cluster, Randomized Controlled Trial.Can J Psychiatry. 2017 May;62(5):327-335. doi: 10.1177/0706743716686919. Epub 2017 Jan 17. Can J Psychiatry. 2017. PMID: 28095259 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Novel Augmentation Strategies in Major Depression.Dan Med J. 2017 Apr;64(4):B5338. Dan Med J. 2017. PMID: 28385173 Review.
-
Depression.Prim Care. 1999 Jun;26(2):211-24. doi: 10.1016/s0095-4543(08)70003-4. Prim Care. 1999. PMID: 10318745 Review.
Cited by
-
An initiative to improve mental health practice in primary care in Caribbean countries.Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2023 Jun 23;47:e89. doi: 10.26633/RPSP.2023.89. eCollection 2023. Rev Panam Salud Publica. 2023. PMID: 37363624 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Murray CJL, Barber RM, Foreman KJ, Ozgoren AA, Abd-Allah F, Abera SF, et al. Global, regional, and national disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) for 306 diseases and injuries and healthy life expectancy (HALE) for 188 countries, 1990–2013: quantifying the epidemiological transition. Lancet. 2015;386:2145–2191. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)61340-X. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Depression in Europe [Internet]. 2012 [cited 2018 May 26]. Available from: http://www.euro.who.int/en/health-topics/noncommunicable-diseases/mental...
-
- Lim K-L, Jacobs P, Ohinmaa A, Schopflocher D, Dewa CS. A new population-based measure of the economic burden of mental illness in Canada. Chronic Dis Can. 2008;28:92–98. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous