Patient and observer reported outcome measures to evaluate health-related quality of life in inherited metabolic diseases: a scoping review
- PMID: 30486833
- PMCID: PMC6263554
- DOI: 10.1186/s13023-018-0953-9
Patient and observer reported outcome measures to evaluate health-related quality of life in inherited metabolic diseases: a scoping review
Abstract
Background: Health-related Quality of Life (HrQoL) is a multidimensional measure, which has gained clinical and social relevance. Implementation of a patient-centred approach to both clinical research and care settings, has increased the recognition of patient and/or observer reported outcome measures (PROMs or ObsROMs) as informative and reliable tools for HrQoL assessment. Inherited Metabolic Diseases (IMDs) are a group of heterogeneous conditions with phenotypes ranging from mild to severe and mostly lacking effective therapies. Consequently, HrQoL evaluation is particularly relevant.
Objectives: We aimed to: (1) identify patient and/or caregiver-reported HrQoL instruments used among IMDs; (2) identify the main results of the application of each HrQoL tool and (3) evaluate the main limitations of HrQoL instruments and study design/methodology in IMDs.
Methods: A scoping review was conducted using methods outlined by Arksey and O'Malley. Additionally, we critically analysed each article to identify the HrQoL study drawbacks.
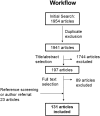
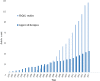
Results: Of the 1954 studies identified, 131 addressed HrQoL of IMDs patients using PROMs and/or ObsROMs, both in observational or interventional studies. In total, we identified 32 HrQoL instruments destined to self- or proxy-completion; only 2% were disease-specific. Multiple tools (both generic and disease-specific) proved to be responsive to changes in HrQoL; the SF-36 and PedsQL questionnaires were the most frequently used in the adult and pediatric populations, respectively. Furthermore, proxy data often demonstrated to be a reliable approach complementing self-reported HrQoL scores. Nevertheless, numerous limitations were identified especially due to the rarity of these conditions.
Conclusions: HrQoL is still not frequently assessed in IMDs. However, our results show successful examples of the use of patient-reported HrQoL instruments in this field. The importance of HrQoL measurement for clinical research and therapy development, incites to further research in HrQoL PROMs' and ObsROMs' creation and validation in IMDs.
Keywords: Health-related quality of life (HrQoL); Inherited metabolic disease(s) (IMD(s)); Observer reported outcome measures (ObsROMs); Patient reported outcome measures (PROMs); Quality of life (QoL).
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
V.R.F is the president and founder of the Portuguese Association for Congenital Disorders of Glycosylation. A.R. is the president of Glycomine, Inc. The costs regarding this publication were covered by Glycomine, Inc. All other authors declare no conflict of interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
References
-
- Bonner N, Abetz-Webb L, Renault L, Caballero T, Longhurst H, Maurer M, et al. Development and content validity testing of a patient-reported outcomes questionnaire for the assessment of hereditary angioedema in observational studies. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2015;13:1–15. doi: 10.1186/s12955-015-0292-7. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Healthy People 2020 . Health-Related Quality of Life and Well-Being. 2010.
-
- FDA. Guidance for Industry Patient-Reported Outcome Measures: Use in Medical Product Development to Support Labeling Claims Clinical/Medical Guidance for Industry Patient-Reported Outcome Measures: Use in Medical Product Development to Support Labeling Claims. Health Qual Life Outcomes. 2006;4:79. 10.1186/1477-7525-4-79. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

