UBL domain of Usp14 and other proteins stimulates proteasome activities and protein degradation in cells
- PMID: 30487212
- PMCID: PMC6294929
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1808731115
UBL domain of Usp14 and other proteins stimulates proteasome activities and protein degradation in cells
Erratum in
-
Correction for Kim and Goldberg, UBL domain of Usp14 and other proteins stimulates proteasome activities and protein degradation in cells.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Jan 22;116(4):1459. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1822051116. Epub 2019 Jan 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 30642963 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
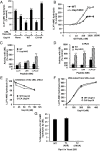
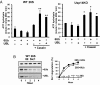
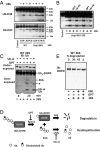
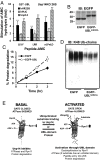
The best-known function of ubiquitin-like (UBL) domains in proteins is to enable their binding to 26S proteasomes. The proteasome-associated deubiquitinating enzyme Usp14/UBP6 contains an N-terminal UBL domain and is an important regulator of proteasomal activity. Usp14 by itself represses multiple proteasomal activities but, upon binding a ubiquitin chain, Usp14 stimulates these activities and promotes ubiquitin-conjugate degradation. Here, we demonstrate that Usp14's UBL domain alone mimics this activation of proteasomes by ubiquitin chains. Addition of this UBL domain to purified 26S proteasomes stimulated the same activities inhibited by Usp14: peptide entry and hydrolysis, protein-dependent ATP hydrolysis, deubiquitination by Rpn11, and the degradation of ubiquitinated and nonubiquitinated proteins. Thus, the binding of Usp14's UBL (apparently to Rpn1's T2 site) seems to mediate the activation of proteasomes by ubiquitinated substrates. However, the stimulation of these various activities was greater in proteasomes lacking Usp14 than in wild-type particles and thus is a general response that does not involve some displacement of Usp14. Furthermore, the UBL domains from hHR23 and hPLIC1/UBQLN1 also stimulated peptide hydrolysis, and the expression of hHR23A's UBL domain in HeLa cells stimulated overall protein degradation. Therefore, many UBL-containing proteins that bind to proteasomes may also enhance allosterically its proteolytic activity.
Keywords: UBL domain; Usp14/Ubp6; hHR23/Rad23; hPLIC/ubiquilin; proteasome activation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Kisselev AF, et al. The caspase-like sites of proteasomes, their substrate specificity, new inhibitors and substrates, and allosteric interactions with the trypsin-like sites. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:35869–35877. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

