Estrogen Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Suppresses Gluconeogenesis via the Transcription Factor Foxo1
- PMID: 30487265
- PMCID: PMC6341301
- DOI: 10.2337/db18-0638
Estrogen Improves Insulin Sensitivity and Suppresses Gluconeogenesis via the Transcription Factor Foxo1
Abstract
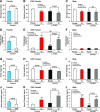
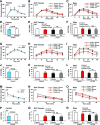
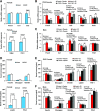
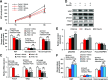
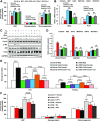
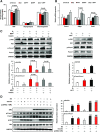
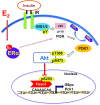
Premenopausal women exhibit enhanced insulin sensitivity and reduced incidence of type 2 diabetes (T2D) compared with age-matched men, but this advantage disappears after menopause with disrupted glucose homeostasis, in part owing to a reduction in circulating 17β-estradiol (E2). Fasting hyperglycemia is a hallmark of T2D derived largely from dysregulation of hepatic glucose production (HGP), in which Foxo1 plays a central role in the regulation of gluconeogenesis. Here, we investigated the action of E2 on glucose homeostasis in male and ovariectomized (OVX) female control and liver-specific Foxo1 knockout (L-F1KO) mice and sought to understand the mechanism by which E2 regulates gluconeogenesis via an interaction with hepatic Foxo1. In both male and OVX female control mice, subcutaneous E2 implant improved insulin sensitivity and suppressed gluconeogenesis; however, these effects of E2 were abolished in L-F1KO mice of both sexes. In our use of mouse primary hepatocytes, E2 suppressed HGP and gluconeogenesis in hepatocytes from control mice but failed in hepatocytes from L-F1KO mice, suggesting that Foxo1 is required for E2 action on the suppression of gluconeogenesis. We further demonstrated that E2 suppresses hepatic gluconeogenesis through activation of estrogen receptor (ER)α-phosphoinositide 3-kinase-Akt-Foxo1 signaling, which can be independent of insulin receptor substrates 1 and 2 (Irs1 and Irs2), revealing an important mechanism for E2 in the regulation of glucose homeostasis. These results may help explain why premenopausal women have lower incidence of T2D than age-matched men and suggest that targeting ERα can be a potential approach to modulate glucose metabolism and prevent diabetes.
© 2018 by the American Diabetes Association.
Figures
References
-
- Danaei G, Finucane MM, Lu Y, et al.; Global Burden of Metabolic Risk Factors of Chronic Diseases Collaborating Group (Blood Glucose) . National, regional, and global trends in fasting plasma glucose and diabetes prevalence since 1980: systematic analysis of health examination surveys and epidemiological studies with 370 country-years and 2·7 million participants. Lancet 2011;378:31–40 - PubMed
-
- Salpeter SR, Walsh JM, Ormiston TM, Greyber E, Buckley NS, Salpeter EE. Meta-analysis: effect of hormone-replacement therapy on components of the metabolic syndrome in postmenopausal women. Diabetes Obes Metab 2006;8:538–554 - PubMed
-
- Misso ML, Murata Y, Boon WC, Jones ME, Britt KL, Simpson ER. Cellular and molecular characterization of the adipose phenotype of the aromatase-deficient mouse. Endocrinology 2003;144:1474–1480 - PubMed
-
- Louet J-F, LeMay C, Mauvais-Jarvis F. Antidiabetic actions of estrogen: insight from human and genetic mouse models. Curr Atheroscler Rep 2004;6:180–185 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

