Role of Forkhead Box O Transcription Factors in Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Dysfunction: Possible Therapeutic Target for Osteoarthritis?
- PMID: 30487470
- PMCID: PMC6321605
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19123794
Role of Forkhead Box O Transcription Factors in Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Dysfunction: Possible Therapeutic Target for Osteoarthritis?
Abstract
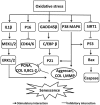
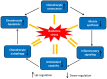
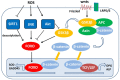
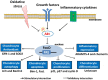
Chondrocyte dysfunction occurs during the development of osteoarthritis (OA), typically resulting from a deleterious increase in oxidative stress. Accordingly, strategies for arresting oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte dysfunction may lead to new potential therapeutic targets for OA treatment. Forkhead box O (FoxO) transcription factors have recently been shown to play a protective role in chondrocyte dysfunction through the regulation of inflammation, autophagy, aging, and oxidative stress. They also regulate growth, maturation, and matrix synthesis in chondrocytes. In this review, we discuss the recent progress made in the field of oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte dysfunction. We also discuss the protective role of FoxO transcription factors as potential molecular targets for the treatment of OA. Understanding the function of FoxO transcription factors in the OA pathology may provide new insights that will facilitate the development of next-generation therapies to prevent OA development and to slow OA progression.
Keywords: FoxO; aging; articular cartilage; autophagy; chondrocyte dysfunction; molecular target; osteoarthritis; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Dysregulated FOXO transcription factors in articular cartilage in aging and osteoarthritis.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014 Jan;22(1):162-70. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2013.11.004. Epub 2013 Nov 21. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2014. PMID: 24269635 Free PMC article.
-
Adenosine A2A receptor signaling promotes FoxO associated autophagy in chondrocytes.Sci Rep. 2021 Jan 13;11(1):968. doi: 10.1038/s41598-020-80244-x. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 33441836 Free PMC article.
-
C10orf10/DEPP activates mitochondrial autophagy and maintains chondrocyte viability in the pathogenesis of osteoarthritis.FASEB J. 2022 Feb;36(2):e22145. doi: 10.1096/fj.202100896R. FASEB J. 2022. PMID: 34997944
-
Oxidative stress, autophagy, epigenetic changes and regulation by miRNAs as potential therapeutic targets in osteoarthritis.Biochem Pharmacol. 2016 May 15;108:1-10. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2015.12.012. Epub 2015 Dec 19. Biochem Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26711691 Review.
-
Targeted regulation of FoxO1 in chondrocytes prevents age-related osteoarthritis via autophagy mechanism.J Cell Mol Med. 2022 Jun;26(11):3075-3082. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17319. Epub 2022 May 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2022. PMID: 35560791 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Antibiotic Treatment Prior to Injury Improves Post-Traumatic Osteoarthritis Outcomes in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Sep 3;21(17):6424. doi: 10.3390/ijms21176424. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32899361 Free PMC article.
-
Forkhead box O proteins in chondrocyte aging and diseases.J Orthop Translat. 2025 Aug 10;54:167-179. doi: 10.1016/j.jot.2025.07.011. eCollection 2025 Sep. J Orthop Translat. 2025. PMID: 40822516 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Osteoarthritis and Cartilage Regeneration: Focus on Pathophysiology and Molecular Mechanisms.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 6;20(24):6156. doi: 10.3390/ijms20246156. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31817613 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Compounds and Their Chondroprotective Effects for Osteoarthritis Amelioration: A Focus on Nanotherapeutic Strategies, Epigenetic Modifications, and Gut Microbiota.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 22;16(21):3587. doi: 10.3390/nu16213587. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519419 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senolytic therapy combining Dasatinib and Quercetin restores the chondrogenic phenotype of human osteoarthritic chondrocytes by the release of pro-anabolic mediators.Aging Cell. 2025 Jan;24(1):e14361. doi: 10.1111/acel.14361. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 39402753 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Collins J.A., Wood S.T., Nelson K.J., Rowe M.A., Carlson C.S., Chubinskaya S., Poole L.B., Furdui C.M., Loeser R.F. Oxidative Stress Promotes Peroxiredoxin Hyperoxidation and Attenuates Pro-survival Signaling in Aging Chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016;291:6641–6654. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.693523. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu S.M., Kim S.J. The thymoquinone-induced production of reactive oxygen species promotes dedifferentiation through the ERK pathway and inflammation through the p38 and PI3K pathways in rabbit articular chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015;35:325–332. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.2014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ntoumou E., Tzetis M., Braoudaki M., Lambrou G., Poulou M., Malizos K., Stefanou N., Anastasopoulou L., Tsezou A. Serum microRNA array analysis identifies miR-140-3p, miR-33b-3p and miR-671-3p as potential osteoarthritis biomarkers involved in metabolic processes. Clin. Epigenet. 2017;9:127. doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0428-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

