Role of Forkhead Box O Transcription Factors in Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Dysfunction: Possible Therapeutic Target for Osteoarthritis?
- PMID: 30487470
- PMCID: PMC6321605
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms19123794
Role of Forkhead Box O Transcription Factors in Oxidative Stress-Induced Chondrocyte Dysfunction: Possible Therapeutic Target for Osteoarthritis?
Abstract
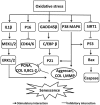
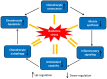
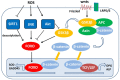
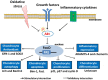
Chondrocyte dysfunction occurs during the development of osteoarthritis (OA), typically resulting from a deleterious increase in oxidative stress. Accordingly, strategies for arresting oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte dysfunction may lead to new potential therapeutic targets for OA treatment. Forkhead box O (FoxO) transcription factors have recently been shown to play a protective role in chondrocyte dysfunction through the regulation of inflammation, autophagy, aging, and oxidative stress. They also regulate growth, maturation, and matrix synthesis in chondrocytes. In this review, we discuss the recent progress made in the field of oxidative stress-induced chondrocyte dysfunction. We also discuss the protective role of FoxO transcription factors as potential molecular targets for the treatment of OA. Understanding the function of FoxO transcription factors in the OA pathology may provide new insights that will facilitate the development of next-generation therapies to prevent OA development and to slow OA progression.
Keywords: FoxO; aging; articular cartilage; autophagy; chondrocyte dysfunction; molecular target; osteoarthritis; oxidative stress.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Collins J.A., Wood S.T., Nelson K.J., Rowe M.A., Carlson C.S., Chubinskaya S., Poole L.B., Furdui C.M., Loeser R.F. Oxidative Stress Promotes Peroxiredoxin Hyperoxidation and Attenuates Pro-survival Signaling in Aging Chondrocytes. J. Biol. Chem. 2016;291:6641–6654. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.693523. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Yu S.M., Kim S.J. The thymoquinone-induced production of reactive oxygen species promotes dedifferentiation through the ERK pathway and inflammation through the p38 and PI3K pathways in rabbit articular chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2015;35:325–332. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2014.2014. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ntoumou E., Tzetis M., Braoudaki M., Lambrou G., Poulou M., Malizos K., Stefanou N., Anastasopoulou L., Tsezou A. Serum microRNA array analysis identifies miR-140-3p, miR-33b-3p and miR-671-3p as potential osteoarthritis biomarkers involved in metabolic processes. Clin. Epigenet. 2017;9:127. doi: 10.1186/s13148-017-0428-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

