Zika Virus Epidemic in Brazil. II. Post-Mortem Analyses of Neonates with Microcephaly, Stillbirths, and Miscarriage
- PMID: 30487475
- PMCID: PMC6306831
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm7120496
Zika Virus Epidemic in Brazil. II. Post-Mortem Analyses of Neonates with Microcephaly, Stillbirths, and Miscarriage
Abstract
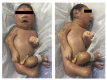
Introduction: The recent Zika virus(ZIKV) epidemic in Brazil was characterized by a range of different clinical presentations, particularly microcephaly, Guillain-Barré syndrome, and death. In this context, we determined the causal relationship between fatal microcephaly cases and ZIKV infection.
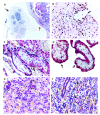
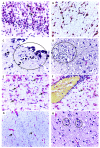
Methods: Twelve fatal cases of neonates, whose mothers were infected with ZIKV during pregnancy, were examined; cases included nine neonatal deaths due to microcephaly, one miscarriage, and two stillbirths. Tissue samples were obtained from all cases at necropsy and were submitted for virological investigation (RT-qPCR and virus isolation) and/or histopathology (hematoxylin and eosin staining) and immunohistochemical assay for the detection of ZIKV antigens.
Results: ZIKV antigens and/or ZIKV RNA were detected in tissue samples of all 12 cases examined. ZIKV was recovered in one case. Results of the virological and immunohistochemical analyses, as well as the anatomic abnormalities and histopathologic changes observed at necropsy on the 12 fatal cases, are presented.
Conclusions: Data from these 12 cases provide strong evidence of the causal relationship between ZIKV and congenital disease in fetuses of women who were infected with the virus during pregnancy.
Keywords: ZIKV RNA; Zika virus; and ZIKV antigen; congenital syndrome; microcephaly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Oehler E., Watrin L., Larre P., Leparc-Goffart I., Lastere S., Valour F., Baudouin L., Mallet H., Musso D., Ghawche F. Zika virus infection complicated by Guillain-Barre syndrome—Case report, French Polynesia, December 2013. Euro Surveill. 2014;19:7–9. doi: 10.2807/1560-7917.ES2014.19.9.20720. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Pan American Health Organization (PAHO)/World Health Organization (WHO) Zika—Epidemiological Update, 25 August 2017. PAHO/WHO; Washington, DC, USA: 2017.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

