A gB/CD3 bispecific BiTE antibody construct for targeting Human Cytomegalovirus-infected cells
- PMID: 30487534
- PMCID: PMC6261951
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-36055-2
A gB/CD3 bispecific BiTE antibody construct for targeting Human Cytomegalovirus-infected cells
Abstract
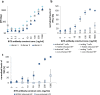
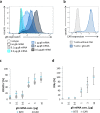
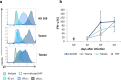
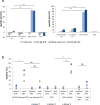
Bispecific T cell engager (BiTE) antibody constructs are successfully used as cancer therapeutics. We hypothesized that this treatment strategy could also be applicable for therapy of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) infection, since HCMV-encoded proteins are abundantly expressed on the surface of infected cells. Here we show that a BiTE antibody construct directed against HCMV glycoprotein B (gB) and CD3 efficiently triggers T cells to secrete IFN-γ and TNF upon co-culture with fibroblasts infected with HCMV strain AD169, Towne or Toledo. Titration of gB expression levels in non-infected cells confirmed that already low levels of gB are sufficient for efficient triggering of T cells in presence of the BiTE antibody construct. Comparison of redirecting T cells with the bispecific antibody versus a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) based on the same scFv showed a similar sensitivity for gB expression. Although lysis of infected target cells was absent, the BiTE antibody construct inhibited HCMV replication by triggering cytokine production. Notably, even strongly diluted supernatants of the activated T cells efficiently blocked the replication of HCMV in infected primary fibroblasts. In summary, our data prove the functionality of the first BiTE antibody construct targeting an HCMV-encoded glycoprotein for inhibiting HCMV replication in infected cells.
Conflict of interest statement
W.H., A.E., M.L., C.B., J. Pr., N.T. and B.S. declare no competing financial or non-financial interests. J.B., M.M. and J. Pe. are employees of AMGEN Research Munich GmbH and have equity positions in Amgen Inc. AMGEN is focused on the development of BiTE antibody constructs for the treatment of malignant diseases.
Figures

References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

