Production of extracellular superoxide and hydrogen peroxide by five marine species of harmful bloom-forming algae
- PMID: 30487659
- PMCID: PMC6247809
- DOI: 10.1093/plankt/fby043
Production of extracellular superoxide and hydrogen peroxide by five marine species of harmful bloom-forming algae
Abstract
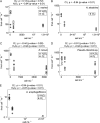
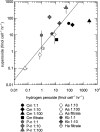
Harmful bloom-forming algae include some of the most prolific microbial producers of extracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). However, the taxonomic diversity of ROS production, the underlying physiological mechanisms and ecophysiological roles of ROS cycling are not completely characterized among phytoplankton taxa that form harmful algal blooms (HABs). This study examines the extracellular production of the ROS superoxide and hydrogen peroxide by five marine HAB species: Chattonella marina, Heterosigma akashiwo, Karenia brevis, Pseudo-nitzschia sp. and Aureococcus anophagefferens. All species produced extracellular superoxide and hydrogen peroxide. Rates of ROS production per cell spanned several orders of magnitude and varied inversely with cell density, suggesting a potential signaling role for extracellular ROS. ROS production was also detected in the spent media of all cultures except K. brevis, indicating the presence of cell-free ROS-generating constituents, such as enzymes or metabolites, which could be further investigated as molecular targets for tracking ROS production in laboratory and field settings. Finally, ratios of superoxide to hydrogen peroxide production could not be accounted for by superoxide dismutation alone, except in the case of K. brevis, indicating a diversity of ROS production and degradation pathways that may ultimately help illuminate the functions of HAB-derived ROS.
Keywords: Aureococcus anophagefferens; Karenia brevis; Pseudo-nitzschia; hydrogen peroxide; reactive oxygen species; superoxide.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Generation of Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) by Harmful Algal Bloom (HAB)-Forming Phytoplankton and Their Potential Impact on Surrounding Living Organisms.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Jan 22;11(2):206. doi: 10.3390/antiox11020206. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35204089 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Production of extracellular reactive oxygen species by phytoplankton: past and future directions.J Plankton Res. 2018 Nov;40(6):655-666. doi: 10.1093/plankt/fby039. Epub 2018 Sep 26. J Plankton Res. 2018. PMID: 30487658 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sublethal and antioxidant effects of six ichthyotoxic algae on early-life stages of the Japanese pearl oyster.Harmful Algae. 2021 Mar;103:102013. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102013. Epub 2021 Mar 26. Harmful Algae. 2021. PMID: 33980452
-
Occurrence of four species of algae in the marine water of Hong Kong.Mar Pollut Bull. 2017 Nov 30;124(2):890-896. doi: 10.1016/j.marpolbul.2016.12.043. Epub 2017 Jan 5. Mar Pollut Bull. 2017. PMID: 28065552
-
Toxic effects, mechanisms, and ecological impacts of harmful algal blooms in China.Harmful Algae. 2022 Jan;111:102148. doi: 10.1016/j.hal.2021.102148. Epub 2021 Dec 4. Harmful Algae. 2022. PMID: 35016761
Cited by
-
Oxidative Stress Regulates a Pivotal Metabolic Switch in Dimethylsulfoniopropionate Degradation by the Marine Bacterium Ruegeria pomeroyi.Microbiol Spectr. 2022 Dec 21;10(6):e0319122. doi: 10.1128/spectrum.03191-22. Epub 2022 Oct 27. Microbiol Spectr. 2022. PMID: 36301115 Free PMC article.
-
Oxidative stress of Microcystis aeruginosa induced by algicidal bacterium Stenotrophomonas sp. KT48.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Jun;106(11):4329-4340. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-11959-2. Epub 2022 May 23. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35604440
-
Light-dependent single-cell heterogeneity in the chloroplast redox state regulates cell fate in a marine diatom.Elife. 2019 Jun 24;8:e47732. doi: 10.7554/eLife.47732. Elife. 2019. PMID: 31232691 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial Heterogeneity in Particle-Associated, Light-Independent Superoxide Production Within Productive Coastal Waters.J Geophys Res Oceans. 2020 Oct;125(10):e2020JC016747. doi: 10.1029/2020JC016747. Epub 2020 Oct 16. J Geophys Res Oceans. 2020. PMID: 33282615 Free PMC article.
-
NADPH-dependent extracellular superoxide production is vital to photophysiology in the marine diatom Thalassiosira oceanica.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019 Aug 13;116(33):16448-16453. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1821233116. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2019. PMID: 31346083 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aldrich D. V. (1962) Photoautotrophy in Gymnodinium breve Davis. Science, 137, 988. - PubMed
-
- Andeer P. F., Learman D. R., McIlvin M., Dunn J. A. and Hansel C. M. (2015) Extracellular haem peroxidases mediate Mn(II) oxidation in a marine Roseobacter bacterium via superoxide production. Environ. Microbiol., 17, 3925–3936. - PubMed
-
- Arzul G., Bodennec G., Gentien P., Bornens P. and Crassous M.-P. (1998) The effect of dissolved oxygen on the haemolytic property of Gymnodinium ichthyotoxins In Reguera B., Blanco J., Fernandez M. L. and Wyatt T. (eds), Harmful Algae. Xunta de Calicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commision of UNESCO, Vigo, Spain, pp. 611–614.
-
- Band-Schmidt C. J., Martinez-Lopez A., Bustillos-Guzman J. J., Carreon-Palau L., Morquecho L., Olguin-Monroy N. O., Zenteno-Savin T., Mendoza-Flores A. et al. (2012) Morphology, biochemistry, and growth of raphidophyte strains from the Gulf of California. Hydrobiologia, 693, 81–97.
-
- Bielski B. H. J., Shiue G. G. and Bajuk S. (1980) Reduction of nitro blue tetrazolium by CO2− and O2− radicals. J. Phys. Chem., 84, 830–833.

