Altered High Density Lipoprotein Composition in Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia
- PMID: 30487733
- PMCID: PMC6246632
- DOI: 10.3389/fnins.2018.00847
Altered High Density Lipoprotein Composition in Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia
Abstract
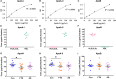
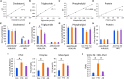
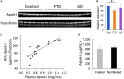
Frontotemporal dementia (FTD) is a common cause of early onset dementia with behavioral variant FTD (bvFTD) being the most common form. bvFTD is characterized clinically by behavioral and personality changes, eating abnormalities, and pathologically, by systemic lipid dysregulation that impacts on survival. As lipoprotein metabolism is at the core of lipid dysregulation, here, we analyzed the composition, both proteins and lipids, of the two major lipoprotein classes in blood - high density lipoproteins (HDLs) and low density lipoproteins (LDLs). Fasted plasmas from bvFTD and Alzheimer's disease (AD) patients and controls were fractionated using fast protein liquid chromatography (FPLC) and samples analyzed by lipid assays, ELISA and western blotting. We found that apolipoprotein A-I (apoA-I) and apolipoprotein A-II (apoA-II) levels in HDLs were decreased in bvFTD compared to controls, whereas apolipoprotein B (apoB) levels in LDLs were unaltered. We also found that cholesterol and triglyceride levels in FPLC fractions were altered in bvFTD compared to controls. The apoB:apoA-I ratio and the standard lipid ratios were significantly increased in bvFTD compared to AD and controls. Furthermore, we found that plasma apolipoprotein C-I and paraoxonase 1 levels were significantly altered in bvFTD and AD, respectively, compared controls. This study represents the first apolipoprotein analysis of bvFTD, and our results suggest altered HDL function and elevated cardiovascular disease risk in bvFTD.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; HDL; LDL; apolipoprotein; biomarker; cardiovascular disease risk; frontotemporal dementia; lipid.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Lipidomics Analysis of Behavioral Variant Frontotemporal Dementia: A Scope for Biomarker Development.Front Neurol. 2018 Feb 28;9:104. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2018.00104. eCollection 2018. Front Neurol. 2018. PMID: 29541056 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma cholesterol in Alzheimer's disease and frontotemporal dementia.Transl Neurosci. 2020 May 18;11(1):116-123. doi: 10.1515/tnsci-2020-0098. eCollection 2020. Transl Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33312717 Free PMC article.
-
Familial and diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in swine. Lipid, ApoB, and ApoA-I concentrations and distributions in plasma and lipoprotein subfractions.Arterioscler Thromb. 1994 Jun;14(6):923-30. doi: 10.1161/01.atv.14.6.923. Arterioscler Thromb. 1994. PMID: 8199183
-
HDL Proteome and Alzheimer's Disease: Evidence of a Link.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Dec 3;9(12):1224. doi: 10.3390/antiox9121224. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 33287338 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lipids and lipoproteins may play a role in the neuropathology of Alzheimer's disease.Front Neurosci. 2023 Nov 16;17:1275932. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1275932. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 38033552 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of APOA-I in Alzheimer's Disease: Bridging Peripheral Tissues and the Central Nervous System.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 May 25;18(6):790. doi: 10.3390/ph18060790. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40573187 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Potential Role of Protein Kinase FAM20C on the Brain in Raine Syndrome, an In Silico Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 17;24(10):8904. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108904. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37240249 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of White Matter Dysfunction and Leukoencephalopathy/Leukodystrophy Genes in the Aetiology of Frontotemporal Dementias: Implications for Novel Approaches to Therapeutics.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 3;22(5):2541. doi: 10.3390/ijms22052541. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33802612 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Elevated ApoB/ApoA-I ratio is associated with acute anti-N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor encephalitis, but not disease outcomes.Front Neurol. 2022 Sep 1;13:896656. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2022.896656. eCollection 2022. Front Neurol. 2022. PMID: 36119695 Free PMC article.
-
Apolipoprotein A1, the neglected relative of Apolipoprotein E and its potential role in Alzheimer's disease.Neural Regen Res. 2021 Nov;16(11):2141-2148. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.310669. Neural Regen Res. 2021. PMID: 33818485 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alam R., Tripathi M., Mansoori N., Parveen S., Luthra K., Lakshmy R., et al. (2014). Synergistic epistasis of paraoxonase 1 (rs662 and rs85460) and apolipoprotein E4 genes in pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease and vascular dementia. Am. J. Alzheimers Dis. Other Demen. 29 769–776. 10.1177/1533317514539541 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

