SeqVItA: Sequence Variant Identification and Annotation Platform for Next Generation Sequencing Data
- PMID: 30487811
- PMCID: PMC6247818
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00537
SeqVItA: Sequence Variant Identification and Annotation Platform for Next Generation Sequencing Data
Abstract
The current trend in clinical data analysis is to understand how individuals respond to therapies and drug interactions based on their genetic makeup. This has led to a paradigm shift in healthcare; caring for patients is now 99% information and 1% intervention. Reducing costs of next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies has made it possible to take genetic profiling to the clinical setting. This requires not just fast and accurate algorithms for variant detection, but also a knowledge-base for variant annotation and prioritization to facilitate tailored therapeutics based on an individual's genetic profile. Here we show that it is possible to provide a fast and easy access to all possible information about a variant and its impact on the gene, its protein product, associated pathways and drug-variant interactions by integrating previously reported knowledge from various databases. With this objective, we have developed a pipeline, Sequence Variants Identification and Annotation (SeqVItA) that provides end-to-end solution for small sequence variants detection, annotation and prioritization on a single platform. Parallelization of the variant detection step and with numerous resources incorporated to infer functional impact, clinical relevance and drug-variant associations, SeqVItA will benefit the clinical and research communities alike. Its open-source platform and modular framework allows for easy customization of the workflow depending on the data type (single, paired, or pooled samples), variant type (germline and somatic), and variant annotation and prioritization. Performance comparison of SeqVItA on simulated data and detection, interpretation and analysis of somatic variants on real data (24 liver cancer patients) is carried out. We demonstrate the efficacy of annotation module in facilitating personalized medicine based on patient's mutational landscape. SeqVItA is freely available at https://bioinf.iiit.ac.in/seqvita.
Keywords: INDELs; NGS; SNPs; annotation; personalized medicine; platform; sequence variants.
Figures



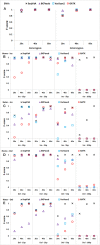
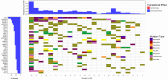
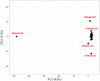
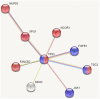

Similar articles
-
iCopyDAV: Integrated platform for copy number variations-Detection, annotation and visualization.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 5;13(4):e0195334. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195334. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29621297 Free PMC article.
-
DaMold: A data-mining platform for variant annotation and visualization in molecular diagnostics research.Hum Mutat. 2017 Jul;38(7):778-787. doi: 10.1002/humu.23227. Epub 2017 May 30. Hum Mutat. 2017. PMID: 28397319
-
Genome analysis and knowledge-driven variant interpretation with TGex.BMC Med Genomics. 2019 Dec 30;12(1):200. doi: 10.1186/s12920-019-0647-8. BMC Med Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31888639 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating massively parallel sequencing into diagnostic workflows and managing the annotation and clinical interpretation challenge.Hum Mutat. 2014 Apr;35(4):413-23. doi: 10.1002/humu.22525. Epub 2014 Mar 6. Hum Mutat. 2014. PMID: 24510514 Review.
-
Bioinformatics Tools and Databases to Assess the Pathogenicity of Mitochondrial DNA Variants in the Field of Next Generation Sequencing.Front Genet. 2018 Dec 11;9:632. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2018.00632. eCollection 2018. Front Genet. 2018. PMID: 30619459 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In Silico Identification and Functional Characterization of Genetic Variations across DLBCL Cell Lines.Cells. 2023 Feb 12;12(4):596. doi: 10.3390/cells12040596. Cells. 2023. PMID: 36831263 Free PMC article.
-
Variant Impact Predictor database (VIPdb), version 2: Trends from 25 years of genetic variant impact predictors.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 28:2024.06.25.600283. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.25.600283. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Hum Genomics. 2024 Aug 28;18(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00663-z. PMID: 38979289 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Best practices for germline variant and DNA methylation analysis of second- and third-generation sequencing data.Hum Genomics. 2024 Nov 5;18(1):120. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00684-8. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39501379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Variant Impact Predictor database (VIPdb), version 2: trends from three decades of genetic variant impact predictors.Hum Genomics. 2024 Aug 28;18(1):90. doi: 10.1186/s40246-024-00663-z. Hum Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39198917 Free PMC article.
-
Knowledge bases and software support for variant interpretation in precision oncology.Brief Bioinform. 2021 Nov 5;22(6):bbab134. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbab134. Brief Bioinform. 2021. PMID: 33971666 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

