Tight near-total corrosive strictures of the proximal esophagus with concomitant involvement of the hypopharynx: Flexible endoscopic management using a novel technique
- PMID: 30487947
- PMCID: PMC6247097
- DOI: 10.4253/wjge.v10.i11.367
Tight near-total corrosive strictures of the proximal esophagus with concomitant involvement of the hypopharynx: Flexible endoscopic management using a novel technique
Abstract
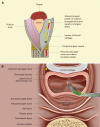
Aim: To investigate the role of a novel minimally invasive endoscopic technique in the management of tight near-total corrosive strictures of the proximal esophagus involving the hypopharynx.
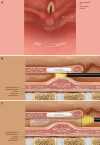
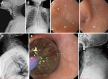
Methods: Two patients with near-total corrosive strictures of the proximal esophagus involving the hypopharynx were managed with the novel endoscopic technique. The technique involved passing a 0.025-inch flexible guide-wire across the stricture, and stricture dilatation, using 10F coaxial diathermy and balloon dilators, followed by electro-incision of the proximal aspect of the residual eccentric stricture by means of a novel approach using a wire-guided sphincterotome.
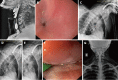
Results: Both patients were successfully managed on an outpatient department basis with the complete relief of symptoms and resolution of strictures on endoscopy and an esophagogram. No adverse events were seen during or after the procedure. There was no recurrence of symptoms at a follow-up of over a year in both cases. There was a significant improvement in the body mass index of both patients after the procedure.
Conclusion: We report a novel flexible endoscopic technique for the management of complex hypopharyngo-esophageal strictures. In experienced hands, the procedure is relatively simple, safe and effective with a durable response.
Keywords: Benign esophageal strictures; Corrosive injury; Cricopharyngeal strictures; Electroincision; Stricture dilatation.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: We, all authors, declare no conflict of interest relevant to this work.
Figures


References
-
- Zargar SA, Kochhar R, Nagi B, Mehta S, Mehta SK. Ingestion of corrosive acids. Spectrum of injury to upper gastrointestinal tract and natural history. Gastroenterology. 1989;97:702–707. - PubMed
-
- Ananthakrishnan N, Parthasarathy G, Maroju NK, Kate V. Sternocleidomastoid muscle myocutaneous flap for corrosive pharyngoesophageal strictures. World J Surg. 2007;31:1592–1596. - PubMed
-
- Wu MH, Tseng YT, Lin MY, Lai WW. Esophageal reconstruction for hypopharyngoesophageal strictures after corrosive injury. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2001;19:400–405. - PubMed
-
- Yannopoulos P, Lytras D, Paraskevas KI. Esophageal reconstruction with intraoperative dilatation of the hypopharynx for the management of chronic corrosive esophageal strictures. A technical tip. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2006;30:940–942. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

