Intermittent systemic hypoxic-hyperoxic training for myocardial protection in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery: first results from a single-centre, randomised controlled trial
- PMID: 30487981
- PMCID: PMC6241980
- DOI: 10.1136/openhrt-2018-000891
Intermittent systemic hypoxic-hyperoxic training for myocardial protection in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery: first results from a single-centre, randomised controlled trial
Abstract
Background: Although remote ischaemic preconditioning (RIP) provides protection against myocardial ischaemia and reperfusion injury during cardiac surgery, it is not widely used. Systemic intermittent hypoxic-hyperoxic training (IHHT) may be a suitable alternative.
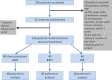
Methods: This is a prospective, single-centre, randomised controlled trial. 127 patients with ischaemic heart disease and indication for coronary artery bypass graft (CABG) surgery from the Cardiology Clinic IM Sechenov First Moscow State Medical University were randomly assigned to IHHT, IHHT-control or RIP. Primary endpoint was serum concentration of troponin I and lactate 2 and 24 hours after surgery.
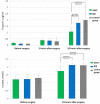
Results: Median value for troponin I 24 hours after surgery was 1.068 (0.388-1.397) ng/mL in the IHHT group and was significantly lower compared with IHHT-controls with 1.980 (1.068-3.239) ng/mL (p=0.012) and to the RIP group with 1.762 (1.288-2.186) ng/mL (p=0.029), while there was no significant difference between RIP and the IHHT-control. Serum lactate after surgery was 1.74 (1.23-2.04) mmol/L in the IHHT group and was also significantly lower compared with IHHT-controls with 2.10 (1.80-2.29) mmol/L (p=0.045) and RIP with 2.12 (1.91-2.33) mmol/L (p=0.032). No significant complications or serious adverse events were observed during IHHT. Intraoperative and early postoperative complications did not differ significantly between groups.
Conclusions: The results of this first trial using IHHT for myocardial protection against perioperative ischaemic myocardial injury in patients undergoing CABG surgery are promising and further larger trials should be done with adequate power to detect clinical rather than surrogate marker benefits.
Keywords: coronary artery bypass surgery; hypoxic-hyperoxic training; myocardial injury; myocardial protection; remote ischemic preconditioning.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: None declared.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardioprotective and prognostic effects of remote ischaemic preconditioning in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery: a single-centre randomised, double-blind, controlled trial.Lancet. 2013 Aug 17;382(9892):597-604. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61450-6. Lancet. 2013. PMID: 23953384 Clinical Trial.
-
Remote ischaemic preconditioning reduces myocardial injury in patients undergoing cardiac surgery with cold-blood cardioplegia: a randomised controlled trial.Heart. 2009 Oct;95(19):1567-71. doi: 10.1136/hrt.2008.155770. Epub 2009 Jun 8. Heart. 2009. PMID: 19508973 Clinical Trial.
-
Intermittent Hypoxic-Hyperoxic Training During Inpatient Rehabilitation Improves Exercise Capacity and Functional Outcome in Patients With Long Covid: Results of a Controlled Clinical Pilot Trial.J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024 Dec;15(6):2781-2791. doi: 10.1002/jcsm.13628. Epub 2024 Nov 19. J Cachexia Sarcopenia Muscle. 2024. PMID: 39559920 Free PMC article.
-
Remote ischaemic preconditioning in coronary artery bypass surgery: a meta-analysis.Heart. 2012 Sep;98(17):1267-71. doi: 10.1136/heartjnl-2011-301551. Heart. 2012. PMID: 22875822 Review.
-
Does intermittent cross-clamp fibrillation provide equivalent myocardial protection compared to cardioplegia in patients undergoing bypass graft revascularisation?Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2009 Nov;9(5):872-8. doi: 10.1510/icvts.2009.209437. Epub 2009 Aug 7. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2009. PMID: 19666649 Review.
Cited by
-
Effects of Hypoxia-Hyperoxia Preconditioning on Indicators of Muscle Damage After Acute Resistance Exercise in Male Athletes.Front Physiol. 2022 Apr 19;13:824210. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.824210. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35514339 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring Hypoxia-Induced Neuroprotection Mechanisms in Post-Stroke Recovery.Transl Stroke Res. 2025 Jul 5. doi: 10.1007/s12975-025-01364-y. Online ahead of print. Transl Stroke Res. 2025. PMID: 40615654 Review.
-
Remote ischemic preconditioning and its role in the prevention of new onset atrial fibrillation post-cardiac surgery. A meta-analysis of randomized control trials.J Arrhythm. 2019 Oct 31;35(6):789-794. doi: 10.1002/joa3.12252. eCollection 2019 Dec. J Arrhythm. 2019. PMID: 31844467 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Intermittent Hypoxia-Hyperoxia on Performance- and Health-Related Outcomes in Humans: A Systematic Review.Sports Med Open. 2022 May 31;8(1):70. doi: 10.1186/s40798-022-00450-x. Sports Med Open. 2022. PMID: 35639211 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Intermittent Hypoxia Conditioning as a New Rehabilitation/ Secondary Prevention Strategy for Patients with Cardiovascular Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis.Curr Cardiol Rev. 2021;17(6):e051121193317. doi: 10.2174/1573403X17666210514005235. Curr Cardiol Rev. 2021. PMID: 33992064 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Thielmann M, Kottenberg E, Kleinbongard P, et al. . Cardioprotective and prognostic effects of remote ischaemic preconditioning in patients undergoing coronary artery bypass surgery: a single-centre randomised, double-blind, controlled trial. Lancet 2013;382:597–604. 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)61450-6 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
