Comparative effectiveness of subcutaneous tocilizumab versus intravenous tocilizumab in a pan-European collaboration of registries
- PMID: 30488002
- PMCID: PMC6241977
- DOI: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000809
Comparative effectiveness of subcutaneous tocilizumab versus intravenous tocilizumab in a pan-European collaboration of registries
Erratum in
-
Correction: Comparative effectiveness of subcutaneous tocilizumab versus intravenous tocilizumab in a pan-European collaboration of registries.RMD Open. 2019 Dec 23;5(2):e000809corr1. doi: 10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000809corr1. eCollection 2019. RMD Open. 2019. PMID: 31921442 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Objective: To compare the real-word effectiveness of subcutaneous tocilizumab (TCZ-SC) and intravenous tocilizumab (TCZ-IV) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
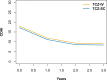
Methods: Patients with RA with TCZ from eight European registries were included. Drug retention was compared using unadjusted Kaplan-Meier and Cox models adjusted for baseline patient, disease and treatment characteristics, using a strata term for year of treatment initiation and country of registry. The proportions of patients achieving Clinical Disease Activity Index (CDAI) remission and low disease activity (LDA) at 1 year were compared using samples matched on the same covariates and corrected for attrition using LUNDEX.
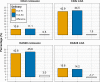
Results: 3448 patients were retrieved, 2414 with TCZ-IV and 1034 with TCZ-SC. Crude median retention was 3.52 years (95% CI 3.22 to 3.85) for TCZ-IV and 2.12 years for TCZ-SC (95% CI 1.88 to 2.38). In a country-stratified and year of treatment initiation-stratified, covariate-adjusted analysis, hazards of discontinuation were similar between TCZ-SC and TCZ-IV treated patients (HR 0.93, 95% CI 0.80 to 1.09). The average adjusted CDAI change at 1 year was similar in both groups (-6.08). After matching, with 560 patients in each group, CDAI remission corrected for attrition at 1 year was also similar between TCZ-SC and TCZ-IV (10.4% in TCZ-IV vs 12.8% in TCZ-SC (difference: 2.4%, bootstrap 95% CI -2.1% to 7.6%)), but CDAI LDA was lower in TCZ-IV patients: 41.0% in TCZ-IV versus 49.1% in TCZ-SC (difference: 8.0 %; bootstrap 95% CI 2.4% to 12.4%).
Conclusion: With similar retention and effectiveness, TCZ-SC is an adequate alternative to TCZ-IV for RA. When possible, considering the costs of the TCZ-IV route, TCZ-SC should be the preferred mode of administration.
Keywords: DMARDs; biological therapies; epidemiology; intravenous; rheumatoid arthritis; subcutaneous; tocilizumab.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: KL: none declared. DM: none declared. FI: none declared. EKK: none declared. TKK has received fees for speaking and/or consulting from AbbVie, BMS, Celgene, Celltrion, Eli Lilly, Hospira, Merck-Serono, MSD, Orion Pharma, Pfizer, Roche, Sandoz and UCB, and received research funding to Diakonhjemmet Hospital from AbbVie, BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Roche and UCB. DN benefited from grant and research support from AbbVie, BMS, MSD, Pfizer, Roche and UCB, and has received fees for speaking and/or consulting for AbbVie, BMS, MSD, Roche, UCB and Pfizer. KP benefited from grant and research support from AbbVie, Roche, Medis, MSD and Pfizer, and has received fees for speaking and/or consulting for AbbVie, Roche, Amgen, MSD, BMS, UCB and Egis. MP-S: none declared. ZR: none declared. MJS: none declared. CC: has received speaker and consulting fees from AbbVie, Amgen, Angellini, Astra Zeneca, BMS, Egis, MSD, Pfizer, Richter, Roche, Sanofi, Servier, Teva, UCB and Zentiva. GL has received fees for consulting for BMS, Roche, MSD, AbbVie and Pfizer. DSC has received consulting fees from BMS, Pfizer and Janssen. CG has received fees for speaking and/or consulting from AbbVie, BMS, Roche, Pfizer, Celgene, MSD, Janssen Cilag, Amgen and UCB, and received research funding from Roche, AbbVie, MSD and Pfizer.
Figures

References
-
- Maini RN, Taylor PC, Szechinski J, et al. Double-blind randomized controlled clinical trial of the interleukin-6 receptor antagonist, tocilizumab, in European patients with rheumatoid arthritis who had an incomplete response to methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 2006;54:2817–29. 10.1002/art.22033 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Kremer JM, Blanco R, Brzosko M, et al. Tocilizumab inhibits structural joint damage in rheumatoid arthritis patients with inadequate responses to methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 2011;63:609–21. - PubMed
-
- European Medicines Agency RoActemra.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
