The Prognosis of Single Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma Was Distinct from Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage A or B: The Role of Albumin-Bilirubin Grade
- PMID: 30488023
- PMCID: PMC6249598
- DOI: 10.1159/000487407
The Prognosis of Single Large Hepatocellular Carcinoma Was Distinct from Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage A or B: The Role of Albumin-Bilirubin Grade
Abstract
Background/aims: Whether single large hepatocellular carcinoma (SLHCC) is classified as Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) stage A or B is still controversial. We aimed to compare the clinical manifestations, treatment modalities, and prognoses among patients with SLHCC and those in BCLC stage A and B.
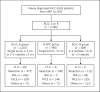
Methods: We enrolled 2,285 treatment-naive hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with BCLC stage A or B from October 2007 to December 2015. Factors in terms of prognoses were analyzed by multivariate analysis.
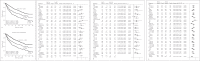
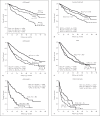
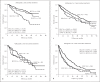
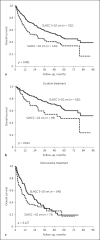
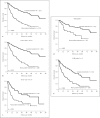
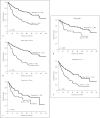
Results: We enrolled 1,210, 466, and 609 patients in a BCLC-A, SLHCC, and BCLC-B group, respectively. After a median follow-up duration of 21.2 months, 898 patients had died. The cumulative 5-year survival rates were 57.0, 42.6, and 27.3% for patients in the BCLC-A, SLHCC, and BCLC-B groups, respectively, which were significantly different (p < 0.001). Multivariate analysis indicated that the following independent risk factors were associated with poor prognosis: age > 65 years, alkaline phosphatase > 100 U/L, creatinine > 1.0 mg/dL, alpha-fetoprotein > 20 mg/mL, noncurative treatment, albumin-bilirubin (ALBI) grade, and HCC staging. Subgroup analysis also confirmed that patients in the SLHCC group had a survival rate intermediate to those in the BCLC-A and BCLC-B groups. However, for patients in the SLHCC group and with ALBI grade 1, outcomes were close to those in the BCLC-A group, especially in the setting of curative treatment. For those with ALBI grades 2 or 3, the prognoses were similar to those of the SLHCC and BCLC-B groups.
Conclusion: Patients in the SLHCC group had an overall survival rate intermediate to those of the BCLC-A and BCLC-B groups. It is suggested that the SLHCC group could be classified as occupying a different stage from the BCLC stages A and B. The ALBI grade could help to stratify SLHCC into a different prognostic group. However, the results need to be validated externally in other regions of the world.
Keywords: Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer stage; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Prognosis; Staging; Tumor size.
Figures
References
-
- Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–E386. - PubMed
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

