Sustainable Access to Antimicrobials; A Missing Component to Antimicrobial Stewardship-A Tale of Two Countries
- PMID: 30488031
- PMCID: PMC6246712
- DOI: 10.3389/fpubh.2018.00324
Sustainable Access to Antimicrobials; A Missing Component to Antimicrobial Stewardship-A Tale of Two Countries
Abstract
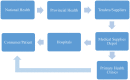
Antimicrobial stewardship encompasses a wide range of processes and interventions designed to ensure that antimicrobials are used in the most effective manner. An important, but often neglected process to include is medicine procurement within hospitals, as the untimely administration of antimicrobials has a direct impact on patient care and antimicrobial resistance. A tender system (an open Request for Proposal, RFP) in South Africa is used in the procurement process to supply medicines and pharmaceutical supplies, whereas in the United States, each hospital is responsible for their own procurement processes. Possible key challenges facing countries to ensure a sustainable medical procurement are poor procurement practices, outdated information systems, and unavailability of human resources to support the current system. This article describes the need for adequate pharmacist-led inventory management systems, for sustainable antimicrobial delivery and the successful implementation of antimicrobial stewardship programs. Strategies to improve inventory control and medication delivery for public sector hospitals in South Africa include the development of national pharmaceutical data management standards. Pharmacist involvement in inventory management principles will ensure that antimicrobials are consistently in adequate supply for patient use, hence promoting safe and effective use while decreasing antimicrobial resistance.
Keywords: antimicrobial resistance; antimicrobial stewardship; international collaboration; pharmacist; stockouts.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Global Worldwide Country Situation Analysis: Response to Antimicrobial Resistance. World Health Organization, Geneva: (2015). Available online at: http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/163468/1/9789241564946_eng.pdf
-
- WHO Global Action Plan on Antimicrobial Resistance. World Health Organization, Geneva: (2015). Available online at: http://www.wpro.who.int/entity/drug_resistance/resources/global_action_p...
-
- WHO Medicine Shortages: Global Approaches to Addressing Shortages of Essential Medicines in Health Systems. (2016). Available online at: www.who.int/medicines/publications/druginformation/WHO_DI_30-2_Medicines...
-
- Stop Stock Outs 2015. Stock Outs National Survey - Third Annual Report South Africa (2016). Available online at: http://www.sahivsoc.org/Files/2015_stock_outs_national_survey.pdf
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources