Comparative Quantification of Arterial Lipid by Intravascular Photoacoustic-Ultrasound Imaging and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy-Intravascular Ultrasound
- PMID: 30488332
- PMCID: PMC6611754
- DOI: 10.1007/s12265-018-9849-2
Comparative Quantification of Arterial Lipid by Intravascular Photoacoustic-Ultrasound Imaging and Near-Infrared Spectroscopy-Intravascular Ultrasound
Abstract
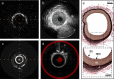
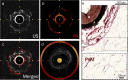
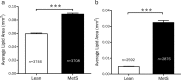
Intravascular photoacoustic-ultrasound (IVPA-US) imaging and near-infrared spectroscopy-intravascular ultrasound (NIRS-IVUS) are two hybrid modalities that detect arterial lipid, with comparison necessary to understand the relative advantages of each. We performed in vivo and ex vivo IVPA-US imaging of the iliac arteries of Ossabaw swine with metabolic syndrome (MetS) and lean swine to investigate sensitivity for early-stage atherosclerosis. We repeated imaging ex vivo with NIRS-IVUS for comparison to IVPA-US and histology. Both modalities showed significantly greater lipid in MetS vs. lean swine, but only IVPA-US localized the lipid as perivascular. To investigate late-stage atherosclerosis, we performed ex vivo IVPA-US imaging of a human coronary artery with comparison to NIRS-IVUS and histology. Two advanced fibroatheromas were identified, with agreement between IVPA-measured lipid area and NIRS-derived lipid content. As confirmed histologically, IVPA-US has sensitivity to detect lipid content similar to NIRS-IVUS and provides additional depth resolution, enabling quantification and localization of lipid cores within plaques.
Keywords: Atherosclerosis; Human; Intravascular imaging; Lipid core plaque; Near-infrared spectroscopy; Perivascular adipose tissue; Photoacoustic imaging; Swine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

