Effects of a histone deacetylase 3 inhibitor on extinction and reinstatement of cocaine self-administration in rats
- PMID: 30488346
- PMCID: PMC6459190
- DOI: 10.1007/s00213-018-5122-2
Effects of a histone deacetylase 3 inhibitor on extinction and reinstatement of cocaine self-administration in rats
Abstract
Rationale: A challenge in treating substance use disorder is that successful treatment often does not persist, resulting in relapse and continued drug seeking. One approach to persistently weaken drug-seeking behaviors is to pair exposure to drug-associated cues or behaviors with delivery of a compound that may strengthen the inhibition of the association between drug cues and behavior.
Objectives: We evaluated whether a selective histone deacetylase 3 (HDAC3) inhibitor could promote extinction and weaken contextual control of operant drug seeking after intravenous cocaine self-administration.
Methods: Male Long-Evans rats received a systemic injection of the HDAC3 inhibitor RGFP966 either before or immediately after the first extinction session. Persistence of extinction was tested over subsequent extinction sessions, as well as tests of reinstatement that included cue-induced reinstatement, contextual renewal, and cocaine-primed reinstatement. Additional extinction sessions occurred between each reinstatement test. We also evaluated effects of RGFP966 on performance and motivation during stable fixed ratio operant responding for cocaine and during a progressive ratio of reinforcement.
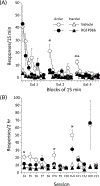
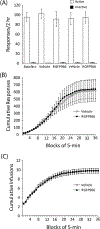
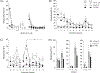
Results: RGFP966 administered before the first extinction session led to significantly less responding during subsequent extinction and reinstatement tests compared to vehicle-injected rats. Follow-up studies found that these effects were not likely due to a performance deficit or a change in motivation to self-administer cocaine, as injections of RGFP966 had no effect on stable responding during a fixed or progressive ratio schedule. In addition, RGFP966 administered just after the first extinction session had no effect during early extinction and reinstatement tests, but weakened long-term responding during later extinction sessions.
Conclusions: These results suggest that a systemic injection of a selective HDAC3 inhibitor can enhance extinction and suppress reinstatement after cocaine self-administration. The finding that behavioral and pharmacological manipulations can be combined to decrease drug seeking provides further potential for treatment by epigenetic modulation.
Keywords: Epigenetics; Extinction; Histone acetylation; Intravenous cocaine; Long-Evans rats.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Statement
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition differentially attenuates cue-induced reinstatement: An interaction of environment and acH3K9 expression in the dorsal striatum.Behav Neurosci. 2019 Oct;133(5):478-488. doi: 10.1037/bne0000333. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31343201 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Drug Relapse.Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Feb 15;89(4):331-338. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33066961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HDAC3-selective inhibitor enhances extinction of cocaine-seeking behavior in a persistent manner.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013 Feb 12;110(7):2647-52. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1213364110. Epub 2013 Jan 7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013. PMID: 23297220 Free PMC article.
-
Blockade of mesolimbic dopamine D3 receptors inhibits stress-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking in rats.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004 Oct;176(1):57-65. doi: 10.1007/s00213-004-1858-y. Epub 2004 Apr 9. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2004. PMID: 15083257 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of cocaine seeking in rats via enhancement of infralimbic cortical activity using stable step-function opsins.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):479-490. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-4964-y. Epub 2018 Jul 12. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30003306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Histone deacetylase inhibition differentially attenuates cue-induced reinstatement: An interaction of environment and acH3K9 expression in the dorsal striatum.Behav Neurosci. 2019 Oct;133(5):478-488. doi: 10.1037/bne0000333. Epub 2019 Jul 25. Behav Neurosci. 2019. PMID: 31343201 Free PMC article.
-
Editorial: the psychopharmacology of extinction-from theory to therapy.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019 Jan;236(1):1-6. doi: 10.1007/s00213-018-5152-9. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2019. PMID: 30604181 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Epigenetic Mechanisms in Drug Relapse.Biol Psychiatry. 2021 Feb 15;89(4):331-338. doi: 10.1016/j.biopsych.2020.08.005. Epub 2020 Aug 14. Biol Psychiatry. 2021. PMID: 33066961 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pharmacological HDAC3 inhibition alters memory updating in young and old male mice.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Jun 26;17:1429880. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1429880. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38989157 Free PMC article.
-
Histone modifications in cocaine, methamphetamine and opioids.Heliyon. 2023 May 19;9(6):e16407. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2023.e16407. eCollection 2023 Jun. Heliyon. 2023. PMID: 37265630 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alaghband Y, Kwapis JL, López AJ, White AO, Aimiuwu OV, Al-Kachak A, … Wood MA (2017). Distinct roles for the deacetylase domain of HDAC3 in the hippocampus and medial prefrontal cortex in the formation and extinction of memory. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 145, 94–104. 10.1016/j.nlm.2017.09.001 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bieszczad KM, Bechay K, Rusche JR, Jacques V, Kudugunti S, Miao W, … Wood MA (2015). Histone Deacetylase Inhibition via RGFP966 Releases the Brakes on Sensory Cortical Plasticity and the Specificity of Memory Formation. The Journal of Neuroscience, 35(38), 13124–32. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0914-15.2015 - DOI - PMC - PubMed

