Lamin A mutation impairs interaction with nucleoporin NUP155 and disrupts nucleocytoplasmic transport in atrial fibrillation
- PMID: 30488537
- PMCID: PMC6440547
- DOI: 10.1002/humu.23691
Lamin A mutation impairs interaction with nucleoporin NUP155 and disrupts nucleocytoplasmic transport in atrial fibrillation
Abstract
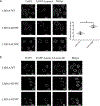
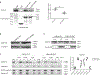
Atrial fibrillation (AF) is the most common cardiac arrhythmia. Here, we show the identification and functional characterization of one AF-associated mutation p.Arg399Cys in lamin A/C. Co-immunoprecipitation and GST pull-down assays demonstrate that lamin A/C interacts with NUP155, which is a nucleoporin and causes AF when mutated. Lamin A/C mutation p.Arg399Cys impairs the interaction between lamin A/C and NUP155, and increases extractability of NUP155 from the nuclear envelope (NE). Mutation p.Arg399Cys leads to aggregation of lamin A/C in the nucleus, although it does not impair the integrity of NE upon cellular stress. Mutation p.Arg399Cys inhibits the export of HSP70 mRNA and the nuclear import of HSP70 protein. Electrophysiological studies show that mutation p.Arg399Cys decreases the peak cardiac sodium current by decreasing the cell surface expression level of cardiac sodium channel Nav 1.5, but does not affect IKr potassium current. In conclusion, our results indicate that lamin A/C mutation p.Arg399Cys weakens the interaction between nuclear lamina (lamin A/C) and the nuclear pore complex (NUP155), leading to the development of AF. The findings provide a novel molecular mechanism for the pathogenesis of AF.
Keywords: LMNA; NUP155; SCN5A/Nav1.5; atrial fibrillation (AF); mutation.
© 2018 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Conflict of interest statement
CONFLICTS OF INTEREST
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


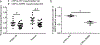
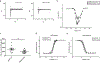
Similar articles
-
Mutation in nuclear pore component NUP155 leads to atrial fibrillation and early sudden cardiac death.Cell. 2008 Dec 12;135(6):1017-27. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.10.022. Cell. 2008. PMID: 19070573
-
The nucleoporin Nup88 is interacting with nuclear lamin A.Mol Biol Cell. 2011 Apr;22(7):1080-90. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E10-05-0463. Epub 2011 Feb 2. Mol Biol Cell. 2011. PMID: 21289091 Free PMC article.
-
Nuclear protein import is reduced in cells expressing nuclear envelopathy-causing lamin A mutants.Exp Cell Res. 2009 Aug 15;315(14):2373-85. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.05.003. Epub 2009 May 12. Exp Cell Res. 2009. PMID: 19442658
-
Crossing the nuclear envelope: hierarchical regulation of nucleocytoplasmic transport.Science. 2007 Nov 30;318(5855):1412-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1142204. Science. 2007. PMID: 18048681 Review.
-
Cytoskeletal Protein Variants Driving Atrial Fibrillation: Potential Mechanisms of Action.Cells. 2022 Jan 25;11(3):416. doi: 10.3390/cells11030416. Cells. 2022. PMID: 35159226 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Genetics and Epigenetics of Atrial Fibrillation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Aug 10;21(16):5717. doi: 10.3390/ijms21165717. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32784971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KLF15 Loss-of-Function Mutation Underlying Atrial Fibrillation as well as Ventricular Arrhythmias and Cardiomyopathy.Genes (Basel). 2021 Mar 12;12(3):408. doi: 10.3390/genes12030408. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33809104 Free PMC article.
-
The Challenges of Diagnosis and Treatment of Arrhythmogenic Cardiomyopathy: Are We there yet?Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022 Aug 15;23(8):283. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2308283. eCollection 2022 Aug. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2022. PMID: 39076647 Free PMC article.
-
Lamin regulates the dietary restriction response via the mTOR pathway in Caenorhabditis elegans.J Cell Sci. 2021 Sep 1;134(17):jcs258428. doi: 10.1242/jcs.258428. Epub 2021 Sep 6. J Cell Sci. 2021. PMID: 34383046 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Nuclear Lamin A/C in the Regulation of Nav1.5 Channel and Microtubules: Lesson From the Pathogenic Lamin A/C Variant Q517X.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Jun 29;10:918760. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.918760. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 35846372 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adhikari AS, Sridhar Rao K, Rangaraj N, Parnaik VK, & Mohan Rao C (2004). Heat stress-induced localization of small heat shock proteins in mouse myoblasts: Intranuclear lamin A/C speckles as target for alphaB-crystallin and Hsp25. Experimental Cell Research, 299(2), 393–403. 10.1016/j.yexcr.2004.05.032 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arimura T, Helbling-Leclerc A, Massart C, Varnous S, Niel F, Lacene E, … Bonne G (2005). Mouse model carrying H222P-Lmna mutation develops muscular dystrophy and dilated cardiomyopathy similar to human striated muscle laminopathies. Human Molecular Genetics, 14(1), 155–169. 10.1093/hmg/ddi017 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- 2016 Top-Notch Innovative Talent Development Project from the Bureau of Human Resources and Social Security of Wuhan City/International
- 91439129/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- R01 HL126729/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2012CB517801/Chinese National Basic Research Programs/International
- 81630002/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81070080/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- R01 HL094498/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- 2014CFA074/Hubei Province Natural Science Key Program/International
- 31430047/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81270162/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2013CB531101/Chinese National Basic Research Programs/International
- 81370206/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 2011ZX09307-001-09/Hubei Province's Outstanding Medical Academic Leader Program Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education from the Ministry of Education, and the "Innovative Development of New Drugs" Key Scientific Project/International
- R01 HL121358/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

