Divergent Synthesis of Natural Derivatives of (+)-Saxitoxin Including 11-Saxitoxinethanoic Acid
- PMID: 30488599
- PMCID: PMC6426452
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.201811717
Divergent Synthesis of Natural Derivatives of (+)-Saxitoxin Including 11-Saxitoxinethanoic Acid
Abstract
The bis-guanidinium toxins are a collection of natural products that display nanomolar potency against select isoforms of eukaryotic voltage-gated Na+ ion channels. We describe a synthetic strategy that enables access to four of these poisons, namely 11-saxitoxinethanoic acid, C13-acetoxy saxitoxin, decarbamoyl saxitoxin, and saxitoxin. Highlights of this work include an unusual Mislow-Evans rearrangement and a late-stage Stille ketene acetal coupling. The IC50 value of 11-saxitoxinethanoic acid was measured against rat NaV 1.4, and found to be 17.0 nm, similar to those of the sulfated toxins gonyautoxin II and III.
Keywords: Stille coupling; guanidinium toxins; rearrangement; sodium channels; sulfoxide.
© 2019 Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. KGaA, Weinheim.
Figures
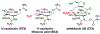





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

