Temporal and regional progression of Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in 3xTg-AD mice
- PMID: 30488653
- PMCID: PMC6351836
- DOI: 10.1111/acel.12873
Temporal and regional progression of Alzheimer's disease-like pathology in 3xTg-AD mice
Abstract
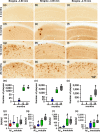
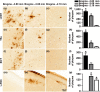
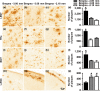
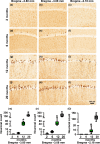
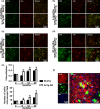
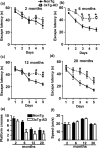
Accumulation of amyloid-β (Aβ) and fibrillary tangles, as well as neuroinflammation and memory loss, are hallmarks of Alzheimer's disease (AD). After almost 15 years from their generation, 3xTg-AD mice are still one of the most used transgenic models of AD. Converging evidence indicates that the phenotype of 3xTg-AD mice has shifted over the years and contradicting reports about onset of pathology or cognitive deficits are apparent in the literature. Here, we assessed Aβ and tau load, neuroinflammation, and cognitive changes in 2-, 6-, 12-, and 20-month-old female 3xTg-AD and nontransgenic (NonTg) mice. We found that ~80% of the mice analyzed had Aβ plaques in the caudal hippocampus at 6 months of age, while 100% of them had Aβ plaques in the hippocampus at 12 months of age. Cortical Aβ plaques were first detected at 12 months of age, including in the entorhinal cortex. Phosphorylated Tau at Ser202/Thr205 and Ser422 was apparent in the hippocampus of 100% of 6-month-old mice, while only 50% of mice showed tau phosphorylation at Thr212/Ser214 at this age. Neuroinflammation was first evident in 6-month-old mice and increased as a function of age. These neuropathological changes were clearly associated with progressive cognitive decline, which was first apparent at 6 months of age and became significantly worse as the mice aged. These data indicate a consistent and predictable progression of the AD-like pathology in female 3xTg-AD mice, and will facilitate the design of future studies using these mice.
Keywords: APP; Aβ; cognitive deficits; inflammation; microglia; neuroinflammation; plaques; tangles; tau; transgenic mice.
© 2018 The Authors. Aging Cell published by the Anatomical Society and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures
References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association (2016). 2016 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer's and Dementia: the Journal of the Alzheimer's Association, 12(4), 459–509. - PubMed
-
- Amin, J. , Paquet, C. , Baker, A. , Asuni, A. A. , Love, S. , Holmes, C. , & Boche, D. (2015). Effect of amyloid‐beta (Abeta) immunization on hyperphosphorylated tau: A potential role for glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)‐3beta. Neuropathology and Applied Neurobiology, 41(4), 445–457. 10.1111/nan.12205 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

