Partial Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy Versus Circumferential Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy for Grade III to IV Prolapsing Hemorrhoids: A Randomized, Noninferiority Trial
- PMID: 30489326
- PMCID: PMC6365260
- DOI: 10.1097/DCR.0000000000001261
Partial Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy Versus Circumferential Stapled Hemorrhoidopexy for Grade III to IV Prolapsing Hemorrhoids: A Randomized, Noninferiority Trial
Abstract
Background: Long-term outcomes and efficacy of partial stapled hemorrhoidopexy are not known.
Objective: The purpose of this study was to compare the long-term clinical efficacy and safety of partial stapled hemorrhoidopexy with circumferential stapled hemorrhoidopexy.
Design: This was a parallel group, randomized, noninferiority clinical trial.
Settings: The study was conducted at a single academic center.
Patients: Patients with grade III/IV hemorrhoids between August 2011 and November 2013 were included.
Interventions: Three hundred patients were randomly assigned to undergo either partial stapled hemorrhoidopexy (group 1, n = 150) or circumferential stapled hemorrhoidopexy (group 2, n = 150).
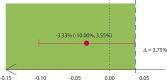
Main outcome measures: The primary outcome was the rate of recurrent prolapse at a median follow-up period of 5 years with a predefined noninferiority margin of 3.75%. Secondary outcomes included incidence and severity of postoperative pain, fecal urgency, anal continence, and the frequency of specific complications, including anorectal stenosis and rectovaginal fistula.
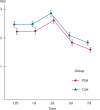
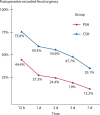
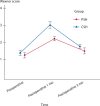
Results: The visual analog scores in group 1 were less than those in group 2 (p < 0.001). Fewer patients in group 1 experienced postoperative urgency compared with those in group 2 (p = 0.001). Anal continence significantly worsened after both procedures, but the difference between preoperative and postoperative continence scores was higher for group 2 than for group 1. Postoperative rectal stenosis did not develop in patients in group 1, although it occurred in 8 patients (5%) in group 2 (p = 0.004). The 5-year cumulative recurrence rate between group 1 (9% (95% CI, 4%-13%)) and group 2 (12% (95% CI, 7%-17%)) did not differ significantly (p = 0.137), and the difference was within the noninferiority margin (absolute difference, -3.33% (95% CI, -10.00% to 3.55%)).
Limitations: The study was limited because it was a single-center trial.
Conclusions: Partial stapled hemorrhoidopexy is noninferior to circumferential stapled hemorrhoidopexy for patients with grade III to IV hemorrhoids at a median follow-up period of 5 years. However, partial stapled hemorrhoidopexy was associated with reduced postoperative pain and urgency, better postoperative anal continence, and minimal risk of rectal stenosis. See Video Abstract at http://links.lww.com/DCR/A790.Trial registration (chictr.org) identifier is chiCTR-trc-11001506.
Figures
References
-
- Longo A. Treatment of hemorrhoidal disease by reduction of mucosa and hemorrhoidal prolapse with a circular suturing device: a new procedure. In: Proceedings of the 6th World Congress of Endoscopic Surgery. 1998:Bologna, Italy: Monduzzi Editore; 777–784..
-
- Shao WJ, Li GC, Zhang ZH, Yang BL, Sun GD, Chen YQ. Systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing stapled haemorrhoidopexy with conventional haemorrhoidectomy. Br J Surg. 2008;95:147–160.. - PubMed
-
- Garg P, Sidhu G, Nair S, et al. The fate and significance of retained staples after stapled haemorrhoidopexy. Colorectal Dis. 2011;13:572–575.. - PubMed
-
- Naldini G. Serious unconventional complications of surgery with stapler for haemorrhoidal prolapse and obstructed defaecation because of rectocoele and rectal intussusception. Colorectal Dis. 2011;13:323–327.. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

