Persistent inflammation and anemia among critically ill septic patients
- PMID: 30489504
- PMCID: PMC6410351
- DOI: 10.1097/TA.0000000000002147
Persistent inflammation and anemia among critically ill septic patients
Abstract
Background: Associations among inflammatory cytokines, erythropoietin (EPO), and anemia in critically ill septic patients remain unclear. This study tested the hypothesis that elevated inflammatory cytokines and decreased EPO would be associated with iron-restricted anemia while accounting for operative blood loss, phlebotomy blood loss, and red blood cell (RBC) transfusion volume.
Methods: Prospective observational cohort study of 42 critically ill septic patients was conducted. Hemoglobin (Hb) at sepsis onset and hospital discharge were used to calculate ΔHb. Operative blood loss, phlebotomy blood loss, and RBC transfusion volume were used to calculate adjusted ΔHb (AdjΔHb) assuming that 300 mL RBC is equal to 1 g/dL Hb. Patients with AdjΔHb of greater than 0 (positive AdjΔHb, n = 18) were compared with patients with AdjΔHb of less than or equal to 0 (negative AdjΔHb, n = 24).
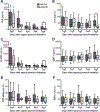
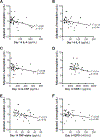
Results: Plasma tumor necrosis factor α, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, EPO, erythrocyte mean corpuscular volume, and serum transferrin receptor were measured on days 0, 1, 4, 7, and 14. Patients with negative AdjΔHb had significantly higher day 14 levels of IL-6 (37.4 vs. 15.2 pg/mL, p < 0.05), IL-8 (39.1 vs. 18.2 pg/mL, p = 0.01), and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (101.3 vs. 60.5 pg/mL, p = 0.01), but not EPO. On linear regression analysis, lower AdjΔHb was associated with higher day 14 levels of IL-6 (r = 0.22, p < 0.01), IL-8 (r = 0.10, p = 0.04), stromal cell-derived factor 1 (r = 0.14, p = 0.02), and tumor necrosis factor α (r = 0.13, p = 0.02), but not EPO. Patients with negative AdjΔHb had significantly lower mean corpuscular volume on days 4 (89.6 vs. 93.2 fL/cell, p = 0.04), 7 (92.3 vs. 94.9 fL/cell, p = 0.04), and 14 (92.1 vs. 96.0 fL/cell, p = 0.03) but similar serum transferrin receptor levels.
Conclusion: Persistent elevation of inflammatory cytokines was associated with iron-restricted anemia among critically ill septic patients, occurring in the absence of systemic iron deficiency, independent of endogenous EPO.
Level of evidence: Prognostic study, level II.
Figures
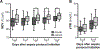
References
-
- Rodriguez RM, Corwin HL, Gettinger A, Corwin MJ, Gubler D, Pearl RG. Nutritional deficiencies and blunted erythropoietin response as causes of the anemia of critical illness. J Crit Care. 2001;16(1):36–41. - PubMed
-
- Vincent JL, Baron JF, Reinhart K, Gattinoni L, Thijs L, Webb A, Meier-Hellmann A, Nollet G, Peres-Bota D, Investigators ABC. Anemia and blood transfusion in critically ill patients. JAMA. 2002;288(12):1499–507. - PubMed
-
- Corwin HL, Parsonnet KC, Gettinger A. RBC transfusion in the ICU. Is there a reason? Chest. 1995;108(3):767–71. - PubMed
-
- Rogiers P, Zhang H, Leeman M, Nagler J, Neels H, Melot C, Vincent JL. Erythropoietin response is blunted in critically ill patients. Intens Care Med. 1997;23(2):159–62. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

