The hepatic artery in orthotopic liver transplantation
- PMID: 3049463
- PMCID: PMC3086426
The hepatic artery in orthotopic liver transplantation
Abstract
Hepatic artery thrombosis (HAT) is a dreadful complication of orthotopic liver transplantation (OLT). This complication occurred in 27 grafts (68% = 27/393 grafts) in 25 patients (9% = 25/313 patients). HAT was responsible for a high mortality (64% = 16/25 patients) despite a high retransplantation rate (70% = 19/27 grafts). HAT should be suspected in case of fulminant liver failure, delayed bile leak or unexplained fever of sepsis of unknown etiology occurring after liver transplantation. Pulsed doppler examination and arteriogram are the decisive diagnostic procedures. Patients presenting HAT can only be rescued by early diagnosis and retransplantation. Aneurysms of the hepatic arterial supply must also be treated urgently, either by conventional vascular repair if possible or by retransplantation, because or the high incidence of fatal rupture (3/4 patients = 75%).
Figures

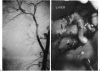
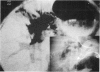



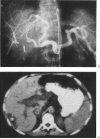
References
-
- Gordon RD, Makowka L, Bronsther MO, Lerut J, Esquivel CO, Iwatsuki S, Starzl TE. Complications of liver transplantation. In: Toledo-Peyrera LH, editor. Complications of organ transplantation. Marcel Dekker Inc.; New York: 1987. pp. 329–354.
-
- Klintmalm GB, Olson LM, Paulsen AW, Whitten CW, Husberg B. Hepatic artery thrombosis after liver transplantation, electromagnetic blood flow evaluation. Transplant. Proc. 1988 in press. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
