Discussion of some 'knowns' and some 'unknowns' about the tumour suppressor p53
- PMID: 30496435
- PMCID: PMC6478126
- DOI: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy077
Discussion of some 'knowns' and some 'unknowns' about the tumour suppressor p53
Abstract
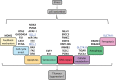
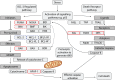
Activation of the tumour suppressor p53 upon cellular stress can induce a number of different cellular processes. The diverse actions of these processes are critical for the protective function of p53 in preventing the development of cancer. However, it is still not fully understood which process(es) activated by p53 is/are critical for tumour suppression and how this might differ depending on the type of cells undergoing neoplastic transformation and the nature of the drivers of oncogenesis. Moreover, it is not clear why upon activation of p53 some cells undergo cell cycle arrest and senescence whereas others die by apoptosis. Here we discuss some of the cellular processes that are crucial for p53-mediated tumour suppression and the factors that could impact cell fate upon p53 activation. Finally, we describe therapies aimed either at activating wild-type p53 or at changing the behaviour of mutant p53 to unleash tumour growth suppressive processes for therapeutic benefit in malignant disease.
Keywords: cell cycle arrest/senescence; cell death; p53; tumour suppression.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Journal of Molecular Cell Biology, IBCB, SIBS, CAS.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Sirtuin1-p53 regulatory axis in aging, cancer and cellular reprogramming.Ageing Res Rev. 2018 May;43:64-80. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2018.02.004. Epub 2018 Feb 21. Ageing Res Rev. 2018. PMID: 29476819 Review.
-
Unravelling mechanisms of p53-mediated tumour suppression.Nat Rev Cancer. 2014 May;14(5):359-70. doi: 10.1038/nrc3711. Epub 2014 Apr 17. Nat Rev Cancer. 2014. PMID: 24739573 Free PMC article.
-
Tumor suppressor p53 and its mutants in cancer metabolism.Cancer Lett. 2015 Jan 28;356(2 Pt A):197-203. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2013.12.025. Epub 2013 Dec 24. Cancer Lett. 2015. PMID: 24374014 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Senescence and aging: the critical roles of p53.Oncogene. 2013 Oct 24;32(43):5129-43. doi: 10.1038/onc.2012.640. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Oncogene. 2013. PMID: 23416979 Review.
-
CD95 ligand induces senescence in mismatch repair-deficient human colon cancer via chronic caspase-mediated induction of DNA damage.Cell Death Dis. 2017 Mar 16;8(3):e2669. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2017.87. Cell Death Dis. 2017. PMID: 28300842 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib Induces p53-Dependent Apoptosis in Activated B Cells.J Immunol. 2024 Jan 1;212(1):154-164. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2300212. J Immunol. 2024. PMID: 37966267 Free PMC article.
-
Myelodysplasia Syndrome, Clonal Hematopoiesis and Cardiovascular Disease.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Apr 19;13(8):1968. doi: 10.3390/cancers13081968. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33921778 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MDM2 Antagonists Induce a Paradoxical Activation of Erk1/2 through a P53-Dependent Mechanism in Dedifferentiated Liposarcomas: Implications for Combinatorial Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Aug 12;12(8):2253. doi: 10.3390/cancers12082253. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32806555 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk of the Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway in the Induction of Apoptosis on Cancer Cells.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021 Aug 28;14(9):871. doi: 10.3390/ph14090871. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34577571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Demethylase-independent function of JMJD2D as a novel antagonist of p53 to promote Liver Cancer initiation and progression.Theranostics. 2020 Jul 11;10(19):8863-8879. doi: 10.7150/thno.45581. eCollection 2020. Theranostics. 2020. PMID: 32754284 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

