Prevention of Injury-Induced Osteoarthritis in Rodent Temporomandibular Joint by Targeting Chondrocyte CaSR
- PMID: 30496623
- PMCID: PMC6482062
- DOI: 10.1002/jbmr.3643
Prevention of Injury-Induced Osteoarthritis in Rodent Temporomandibular Joint by Targeting Chondrocyte CaSR
Abstract
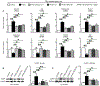
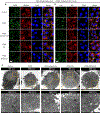
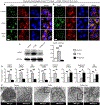
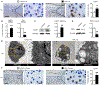
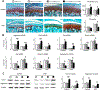
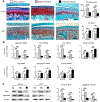
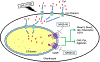
Traumatic joint injuries produce osteoarthritic cartilage manifesting accelerated chondrocyte terminal differentiation and matrix degradation via unknown cellular and molecular mechanisms. Here we report the ability of biomechanical stress to increase expression of the calcium-sensing receptor (CaSR), a pivotal driver of chondrocyte terminal differentiation, in cultured chondrogenic cells subjected to fluid flow shear stress (FFSS) and in chondrocytes of rodent temporomandibular joint (TMJ) cartilage subjected to unilateral anterior cross-bite (UAC). In cultured ATDC5 cells or TMJ chondrocytes, FFSS induced Ca2+ loading and CaSR localization in endoplasmic reticulum (ER), casually accelerating cell differentiation that could be abrogated by emptying ER Ca2+ stores or CaSR knockdown. Likewise, acute chondrocyte-specific Casr knockout (KO) prevented the UAC-induced acceleration of chondrocyte terminal differentiation and matrix degradation in TMJ cartilage in mice. More importantly, local injections of CaSR antagonist, NPS2143, replicated the effects of Casr KO in preventing the development of osteoarthritic phenotypes in TMJ cartilage of the UAC-treated rats. Our study revealed a novel pathological action of CaSR in development of osteoarthritic cartilage due to aberrant mechanical stimuli and supports a therapeutic potential of calcilytics in preventing osteoarthritis in temporomandibular joints by targeting the CaSR. © 2018 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Keywords: CALCIUM-SENSING RECEPTOR; CHONDROCYTE DIFFERENTIATION; DENTAL MALOCCLUSION; OSTEOARTHRITIS; TEMPOROMANDIBULAR JOINT.
© 2018 American Society for Bone and Mineral Research.
Figures
References
-
- Guo FJ, Xiong Z, Lu X, Ye M, Han X, Jiang R 2014. ATF6 upregulates XBP1S and inhibits ER stress-mediated apoptosis in osteoarthritis cartilage. Cell Signal 26(2):332–42. - PubMed
-
- Barley RD, Adesida AB, Bagnall KM, Jomha NM 2010. Immunohistochemical characterization of reparative tissue present in human osteoarthritic tissue. Virchows Arch 456(5): 561–9. - PubMed
-
- Bush JR, Beier F 2013. TGF-beta and osteoarthritis--the good and the bad. Nat Med 19(6):667–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P30 AR066262/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- 81530033/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81700995/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81500896/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81371166/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- R01 DK122259/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- IK6 BX004835/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- U01 AG042139/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AR066160/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG066671/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042124/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR067291/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042145/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- I01 BX003453/BX/BLRD VA/United States
- U01 AG042168/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042140/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- 81470762/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- 81500875/National Natural Science Foundation of China/International
- U01 AG027810/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG061085/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AG042143/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

