B cell homeostasis is maintained during long-duration spaceflight
- PMID: 30496712
- PMCID: PMC6397409
- DOI: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00789.2018
B cell homeostasis is maintained during long-duration spaceflight
Abstract
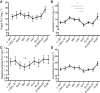
Long-duration spaceflights reportedly induce immune dysregulation, which is considered a risk to astronaut safety and mission success. Recent studies have examined the impact of spaceflight on markers of adaptive and innate immunity, but no study, to date, has comprehensively evaluated humoral immunity and serological markers of B cell function. The aim of this study was to characterize changes in B cell numbers and phenotypes, along with plasma Igs and polyclonal free light chains (FLCs)-near-"real-time" biomarkers of Ig synthesis-in response to an ~6-mo mission to the International Space Station (ISS). Whole-blood samples were collected before flight, during flight ("Early flight," "Mid-flight," and "Late flight"), immediately upon return, and during a recovery period (R + 18, R + 30/R + 33, and R + 60/R + 66) from 23 ISS crew members. B Cell counts and phenotypes were measured throughout the duration of the mission, along with total plasma Ig and FLC levels. There was no effect of spaceflight on the number and proportion of the different B cell subsets. There was no difference in kappa FLC between preflight samples and either in-flight or recovery samples ( P > 0.05), and only a marginal reduction was observed in lambda FLC levels upon return to Earth ( P < 0.05). Furthermore, IgG and IgM remained unchanged during and after spaceflight compared with preflight values ( P > 0.05). Of note, plasma IgA concentrations were elevated in-flight compared with baseline and recovery values ( P < 0.05). These results indicate that B cell homeostasis is maintained during long-duration spaceflight, advocating for potential in-flight vaccination as viable countermeasures against viral reactivation during exploration-class missions.
Keywords: B cell homeostasis; free light chains; immunoglobulins; long-duration spaceflight.
Conflict of interest statement
J. Campbell reports minor shares in Abingdon Health, the company that produces one of the assay (FLC ELISA Kits) used in this project.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NK cell function is impaired during long-duration spaceflight.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019 Apr 1;126(4):842-853. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00761.2018. Epub 2018 Nov 1. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2019. PMID: 30382809
-
Salivary antimicrobial proteins and stress biomarkers are elevated during a 6-month mission to the International Space Station.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020 Feb 1;128(2):264-275. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00560.2019. Epub 2019 Nov 21. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2020. PMID: 31751178 Free PMC article.
-
Prevalence of sleep deficiency and use of hypnotic drugs in astronauts before, during, and after spaceflight: an observational study.Lancet Neurol. 2014 Sep;13(9):904-12. doi: 10.1016/S1474-4422(14)70122-X. Epub 2014 Aug 7. Lancet Neurol. 2014. PMID: 25127232 Free PMC article.
-
Herpes Virus Reactivation in Astronauts During Spaceflight and Its Application on Earth.Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 7;10:16. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00016. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30792698 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune System Dysregulation During Spaceflight: Potential Countermeasures for Deep Space Exploration Missions.Front Immunol. 2018 Jun 28;9:1437. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2018.01437. eCollection 2018. Front Immunol. 2018. PMID: 30018614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-term space missions' effects on the human organism: what we do know and what requires further research.Front Physiol. 2024 Feb 13;15:1284644. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2024.1284644. eCollection 2024. Front Physiol. 2024. PMID: 38415007 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Collection of biospecimens from the inspiration4 mission establishes the standards for the space omics and medical atlas (SOMA).Nat Commun. 2024 Jun 11;15(1):4964. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-48806-z. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38862509 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges for the human immune system after leaving Earth.NPJ Microgravity. 2024 Nov 18;10(1):106. doi: 10.1038/s41526-024-00446-9. NPJ Microgravity. 2024. PMID: 39557881 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microgravity and immune cells.J R Soc Interface. 2023 Feb;20(199):20220869. doi: 10.1098/rsif.2022.0869. Epub 2023 Feb 15. J R Soc Interface. 2023. PMID: 36789512 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Next generation of astronauts or ESA astronaut 2.0 concept and spotlight on immunity.NPJ Microgravity. 2023 Jun 28;9(1):51. doi: 10.1038/s41526-023-00294-z. NPJ Microgravity. 2023. PMID: 37380641 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berkowska MA, Driessen GJ, Bikos V, Grosserichter-Wagener C, Stamatopoulos K, Cerutti A, He B, Biermann K, Lange JF, van der Burg M, van Dongen JJ, van Zelm MC. Human memory B cells originate from three distinct germinal center-dependent and -independent maturation pathways. Blood 118: 2150–2158, 2011. doi:10.1182/blood-2011-04-345579. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

