TLR Signaling Is Activated in Lymph Node-Resident CLL Cells and Is Only Partially Inhibited by Ibrutinib
- PMID: 30498085
- PMCID: PMC6342512
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-0781
TLR Signaling Is Activated in Lymph Node-Resident CLL Cells and Is Only Partially Inhibited by Ibrutinib
Abstract
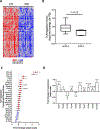
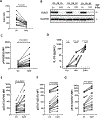
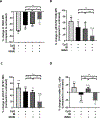
Chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) is a malignancy of mature B cells driven by B-cell receptor (BCR) signaling and activated primarily in the lymph node. The Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) inhibitor ibrutinib effectively inhibits BCR-dependent proliferation and survival signals and has emerged as a breakthrough therapy for CLL. However, complete remissions are uncommon and are achieved only after years of continuous therapy. We hypothesized that other signaling pathways that sustain CLL cell survival are only partially inhibited by ibrutinib. In normal B cells, Toll-like receptor (TLR) signaling cooperates with BCR signaling to activate prosurvival NF-κB. Here, we show that an experimentally validated gene signature of TLR activation is overexpressed in lymph node-resident CLL cells compared with cells in the blood. Consistent with TLR activation, we detected phosphorylation of NF-κB, STAT1, and STAT3 in lymph node-resident CLL cells and in cells stimulated with CpG oligonucleotides in vitro. CpG promoted IRAK1 degradation, secretion of IL10, and extended survival of CLL cells in culture. CpG-induced TLR signaling was significantly inhibited by both an IRAK1/4 inhibitor and ibrutinib. Although inhibition of TLR signaling was incomplete with either drug, the combination achieved superior results, including more effective inhibition of TLR-mediated survival signaling. Our data suggest an important role for TLR signaling in CLL pathogenesis and in sustaining the viability of CLL cells during ibrutinib therapy. The combination of ibrutinib with a TLR pathway inhibitor could provide superior antitumor activity and should be investigated in clinical studies. SIGNIFICANCE: CLL relies on the concomitant cooperation of B-cell receptor and Toll-like receptor signaling; inhibition of both pathways is superior to inhibition of either pathway alone. GRAPHICAL ABSTRACT: http://cancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/canres/79/2/360/F1.large.jpg.
©2018 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest
A. Wiestner reports receiving commercial research grants from Acerta Pharma and Pharmacyclics, an Abbvie Company. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed by the other authors.
Figures



References
-
- Sun C, Wiestner A. Prognosis and therapy of chronic lymphocytic leukemia and small lymphocytic lymphoma. Cancer Treat Res 2015;165:147–75 - PubMed
-
- Damle RN, Wasil T, Fais F, Ghiotto F, Valetto A, Allen SL, et al. Ig V gene mutation status and CD38 expression as novel prognostic indicators in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999;94:1840–7 - PubMed
-
- Hamblin TJ, Davis Z, Gardiner A, Oscier DG, Stevenson FK. Unmutated Ig V(H) genes are associated with a more aggressive form of chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 1999;94:1848–54 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

