An investigation into the efficacy of intra-articular ozone (O2-O3) injection in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 30498370
- PMCID: PMC6207244
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S175441
An investigation into the efficacy of intra-articular ozone (O2-O3) injection in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Purpose: This study aimed to review and pool the current literature on intra-articular ozone injection in knee osteoarthritis (OA) patients.
Methods: A systematic review of three big databases was performed to identify all English-language randomized clinical trials (RCTs) that evaluated the efficacy of intra-articular ozone injection vs a control injection for knee OA sufferers, using the following two measuring tools: pain VAS and Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Arthritis Index (WOMAC).
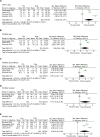
Results: A total of 428 patients in five RCTs were included, from which 53% (n=225) were in the ozone group and 47% in the control (hyaluronic acid [HA], dextrose, and air injection) group (n=203). The mean age of the patients in both groups was 64 years. Females were the majority. All studies had at least 2 months of follow-up (F/U). Mean difference (MD) between the groups for VAS in the first month was -0.23 with a P-value of 0.71 (negative value was in favor of ozone), whereas this difference in the third and sixth months reached 1.04 and 1.31, respectively, favoring the control group. These data demonstrated that control injection had a more prolonged pain relief period. A similar trend was seen regarding WOMAC scores; pooled results showed that ozone was slightly better than the control injections during the first month (MD =-7.84 [P=0.15]), but it declined to MD=2.55 and 8.23 at 2- to 3- and 4- to 6-month F/U, respectively, again in favor of control injections. Also, adverse events occurred homogeneously in both ozone (6/150 cases, 4%) and control groups (7/129 cases, 5.4%; P-value=0.31).
Conclusion: Based on the current meta-analysis, intra-articular ozone injection efficacy was significantly superior to placebo and slightly lower to other control injections with non-significant difference. Therefore, ozone could be recommended as an efficient non-surgical treatment, durable for at least 3-6 months, in mild or moderate knee OA management.
Keywords: hyaluronic acid; knee osteoarthritis; meta-analysis; ozone; systematic review.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures






References
-
- Richmond J, Hunter D, Irrgang J, et al. American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons clinical practice guideline on the treatment of osteoarthritis (OA) of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(4):990–993. - PubMed
-
- Murphy L, Helmick CG. The impact of osteoarthritis in the United States: a population-health perspective. Am J Nurs. 2012;112(3 Suppl 1):S13–S19. - PubMed
-
- Tehrani-Banihashemi A, Davatchi F, Jamshidi AR, Faezi T, Paragomi P, Barghamdi M. Prevalence of osteoarthritis in rural areas of Iran: a WHO-ILAR COPCORD study. Int J Rheum Dis. 2014;17(4):384–388. - PubMed
-
- Mishra SK, Pramanik R, Das P, et al. Role of intra-articular ozone in osteoarthritis of knee for functional and symptomatic improvement. Ind J Phys Med Rehabilit. 2011;22(2):65–69.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

