Mitofusin-2 acts as biomarker for predicting poor prognosis in hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 30498519
- PMCID: PMC6258311
- DOI: 10.1186/s13027-018-0212-7
Mitofusin-2 acts as biomarker for predicting poor prognosis in hepatitis B virus related hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
Objective: To investigate the expression of Mitofusin-2 (MFN2) in HCC tissues and its role in the development of HCC.
Methods: A total of 107 HCC specimens were collected for tissue microarray analysis and immunohistochemistry (IHC) analysis. The relationship between MFN2 expression and clinical features of patients with HCC was analyzed.
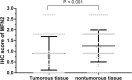
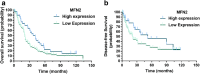
Results: Expression level of MFN2 in HCC tissues was 0.92 ± 0.78, significantly lower than that of matched paracancerous liver tissues (1.25 ± 0.75). Patients with low expression of MFN2 had significantly higher rates of cirrhosis than those with high expression of MFN2 (P = 0.049). Kaplan-Meier survival analysis showed that HCC patients with low expression of MFN2 had a worse prognosis in overall survival than HCC patients with high expression of MFN2 (P = 0.027). Patients with high expression of MFN2 had a better prognosis in disease-free survival compared with HCC patients with low expression of MFN2 (P = 0.047). Vascular invasion and MFN2 expression were shown to be prognostic variables for overall survival in patients with HCC. Multivariate analysis showed that vascular invasion (P < 0.001) and MFN2 expression (P = 0.045) were independent prognostic factors for overall survival. Vascular invasion (P < 0.001) and MFN2 expression (P = 0.042) were independent risk factors associated with disease-free survival.
Conclusion: Our data revealed that MFN2 expression was decreased in HCC samples. High MFN2 expression was correlated with longer survival times in patients with HCC and served as an independent factor for better outcomes. Our study therefore provides a promising biomarker for the prognostic prediction of HCC and a potential therapeutic target for the disease.
Keywords: Biomarker; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Mitofusin-2; Prognosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The study was reviewed and approved by the Medical Ethics Committee of Jining No. 1 People’s Hospital. Since all specimens used were anonymous, the Medical Ethics Committee exempted patients from the need for informed consent.Not applicable.The authors declare that they have no competing interests.Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Decreased expression levels of ELOVL6 indicate poor prognosis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2019 Dec;18(6):6214-6220. doi: 10.3892/ol.2019.10974. Epub 2019 Oct 9. Oncol Lett. 2019. PMID: 31788097 Free PMC article.
-
Altered epidermal fatty acid-binding protein expression in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts unfavorable outcomes.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Nov 23;10:6275-6284. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S181555. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 30538573 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor alpha indicates unfavorable outcomes in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Manag Res. 2018 Jun 26;10:1781-1789. doi: 10.2147/CMAR.S166971. eCollection 2018. Cancer Manag Res. 2018. PMID: 29983595 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic impact of mitofusin 2 expression in colon cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2022 Oct;11(10):3610-3619. doi: 10.21037/tcr-22-589. Transl Cancer Res. 2022. PMID: 36388028 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical significance of mitofusin-2 and its signaling pathways in hepatocellular carcinoma.World J Surg Oncol. 2016 Jul 7;14(1):179. doi: 10.1186/s12957-016-0922-5. World J Surg Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27389277 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mfn2 is responsible for inhibition of the RIG-I/IRF7 pathway and activation of NLRP3 inflammasome in Seneca Valley virus-infected PK-15 cells to promote viral replication.Front Immunol. 2022 Jul 25;13:955671. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.955671. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35958608 Free PMC article.
-
MFN2 suppresses the accumulation of lipid droplets and the progression of clear cell renal cell carcinoma.Cancer Sci. 2024 Jun;115(6):1791-1807. doi: 10.1111/cas.16151. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 38480904 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial alterations and signatures in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025 Feb 18;44(1):34. doi: 10.1007/s10555-025-10251-9. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2025. PMID: 39966277 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of MFN2 alleviates sorafenib-induced cardiomyocyte necroptosis via the MAM-CaMKIIδ pathway in vitro and in vivo.Theranostics. 2022 Jan 1;12(3):1267-1285. doi: 10.7150/thno.65716. eCollection 2022. Theranostics. 2022. PMID: 35154486 Free PMC article.
-
Mitophagy in Cancer: A Tale of Adaptation.Cells. 2019 May 22;8(5):493. doi: 10.3390/cells8050493. Cells. 2019. PMID: 31121959 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. LANCET. 2018. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

