New insights into genetic predisposition and novel therapeutic targets for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
- PMID: 30498712
- PMCID: PMC6230844
- DOI: 10.21037/hbsn.2018.08.05
New insights into genetic predisposition and novel therapeutic targets for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease
Abstract
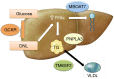
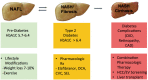
Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is the most common form of chronic liver disease in the United States affecting 80-100 million Americans. NAFLD encompasses a spectrum of diseases ranging from excess liver fat (nonalcoholic fatty liver or NAFL), to necro-inflammation (nonalcoholic steatohepatitis or NASH), to fibrosis/ cirrhosis, and malignant transformation (hepatocellular carcinoma). Susceptibility to NAFLD is highly variable and it remains unclear why some patients with NAFLD exhibit NASH, whereas patients with known risk factors have NAFL only. The reasons for this variability can be a partially attributed to differences in genetic background. In the last decade, there have been multiple genome wide association studies, which have enriched our understanding of the genetic basis of NAFLD. The I148M PNPLA3 (patatin-like phospholipase domain-containing protein 3) variant has been identified as the major common genetic determinant of NAFLD. Variants with moderate effect size like TM6SF2, MBOAT7 and GCKR have also been shown to have a significant contribution. New research has uncovered major pathways leading to disease development and progression; therefore, multiple medications are being developed and tested for the treatment of advanced NAFLD. These agents target metabolic mechanisms as well as inflammation and fibrosis pathways. Several randomized clinical trials (RCTs) are evaluating the efficacy of these novel agents on histological improvement of disease severity and decreasing liver-related outcomes. FDA-approved medications for NASH and NASH-related fibrosis are expected by 2020.
Keywords: Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD); clinical trial; nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH); polymorphism; treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of Interest: N Alkhouri is on the speaker bureau for Intercept Pharmaceuticals and Gilead Sciences and received research funding from Intercept Pharmaceuticals, Allergan, and Gilead Sciences. The other authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Comment in
-
The dawn of a new era for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019 Dec;8(6):629-631. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.09.15. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2019. PMID: 31929991 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
PNPLA3 and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: towards personalized medicine for fatty liver.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2020 Jun;9(3):353-356. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.10.35. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32509828 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) diagnosis and management-differentiating the essential from the ancillary and the present from the future.Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2020 Jun;9(3):374-378. doi: 10.21037/hbsn.2019.11.12. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr. 2020. PMID: 32509834 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
