Increased Autophagy Enhances the Resistance to Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Human Fibroblast-Like Synovial Cell
- PMID: 30498756
- PMCID: PMC6222231
- DOI: 10.1155/2018/4941027
Increased Autophagy Enhances the Resistance to Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha Treatment in Rheumatoid Arthritis Human Fibroblast-Like Synovial Cell
Abstract
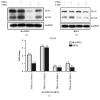
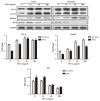
Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha (TNF-α) was reported to increase autophagy in rheumatoid arthritis human fibroblast-like synovial cell (RA-HFLS). We investigated different levels of TNF-α exposed to RA-HFLS by focusing on the relationship of autophagy and apoptosis. RA-HFLS and normal human fibroblast-like synovial cell (HFLS) were stimulated by TNF-α in the presence or the absence of 3-methyladenine (3-MA) or chloroquine (CQ). Cell apoptosis was detected by flow cytometry. Autophagy was determined through the expression levels of LC3, Beclin1, and P62 measured by Western Blot analysis as well as Confocal Laser Scanning Microscopy. The basal autophagy level was significantly higher in RA-HFLS than in HFLS. Autophagy was enhanced both in RA-HFLS and HFLS when they were treated with TNF-α. With the treatment of TNF-α, a slightly higher autophagy level was found in RA-HFLS than in HFLS, without a dose dependent effect. When autophagy was inhibited by 3-MA or CQ, apoptosis increased in both groups. With the stimulation of different doses TNF-α, apoptosis was much higher in HFLS group than in RA-HFLS. Autophagy is a protection mechanism when treated by TNF-α in RA-HFLS.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Silencing aquaporin 1 inhibits autophagy to exert anti-rheumatoid arthritis effects in TNF-α-induced fibroblast-like synoviocytes and adjuvant-induced arthritis rats.Inflamm Res. 2025 Jan 8;74(1):12. doi: 10.1007/s00011-024-01966-6. Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 39774992
-
Survivin promotes rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocyte cell proliferation, and the expression of angiogenesis-related proteins by activating the NOTCH pathway.Int J Rheum Dis. 2021 Jul;24(7):922-929. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.14150. Epub 2021 Jun 7. Int J Rheum Dis. 2021. PMID: 34096679
-
Interleukin (IL)-23 p19 expression induced by IL-1beta in human fibroblast-like synoviocytes with rheumatoid arthritis via active nuclear factor-kappaB and AP-1 dependent pathway.Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007 Aug;46(8):1266-73. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/kem055. Epub 2007 Jun 14. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2007. PMID: 17569750
-
1, 25-dihydroxy-vitamin D3 with tumor necrosis factor-alpha protects against rheumatoid arthritis by promoting p53 acetylation-mediated apoptosis via Sirt1 in synoviocytes.Cell Death Dis. 2016 Oct 20;7(10):e2423. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2016.300. Cell Death Dis. 2016. PMID: 27763638 Free PMC article.
-
[The research development of programmed cell death in rheumatoid arthritis].Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024 Oct 25;76(5):827-840. Sheng Li Xue Bao. 2024. PMID: 39468819 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
The Expression of Inflammasomes NLRP1 and NLRP3, Toll-Like Receptors, and Vitamin D Receptor in Synovial Fibroblasts From Patients With Different Types of Knee Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 19;12:767512. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.767512. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35126351 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolin as a Universal Target in Dermatology.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Dec 20;21(1):80. doi: 10.3390/ijms21010080. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31877626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Apoptosis, Autophagy, NETosis, Necroptosis, and Pyroptosis Mediated Programmed Cell Death as Targets for Innovative Therapy in Rheumatoid Arthritis.Front Immunol. 2021 Dec 24;12:809806. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.809806. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 35003139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Andrographolide Ameliorates Rheumatoid Arthritis by Regulating the Apoptosis-NETosis Balance of Neutrophils.Int J Mol Sci. 2019 Oct 11;20(20):5035. doi: 10.3390/ijms20205035. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31614480 Free PMC article.
-
Study on optimization of extraction and purification processes for total flavonoids from Lycopi herba roots and their anti-proliferative effects on fibrous synoviocytes in human rheumatoid arthritis.Ultrason Sonochem. 2025 Jan;112:107164. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.107164. Epub 2024 Nov 19. Ultrason Sonochem. 2025. PMID: 39579583 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

