Toward Exosome-Based Neuronal Diagnostic Devices
- PMID: 30501125
- PMCID: PMC6315917
- DOI: 10.3390/mi9120634
Toward Exosome-Based Neuronal Diagnostic Devices
Abstract
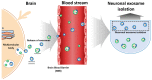
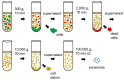
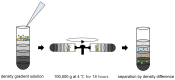
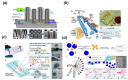
Targeting exosome for liquid biopsy has gained significant attention for its diagnostic and therapeutic potential. For detecting neuronal disease diagnosis such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), the main technique for identifying AD still relies on positron-emission tomography (PET) imaging to detect the presence of amyloid-β (Aβ). While the detection of Aβ in cerebrospinal fluid has also been suggested as a marker for AD, the lack of quantitative measurements has compromised existing assays. In cerebrospinal fluid, in addition to Aβ, T-Tau, and P-Tau, alpha-synuclein has been considered a biomarker of neurodegeneration. This review suggests that and explains how the exosome can be used as a neuronal diagnostic component. To this end, we summarize current progress in exosome preparation/isolation and quantification techniques and comment on the outlooks for neuronal exosome-based diagnostic techniques.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Parkinson’s disease; diagnostics; exosome.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures






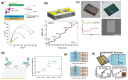

References
-
- Alzheimer’s Association 2017 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2017;13:325–373. doi: 10.1016/j.jalz.2017.02.001. - DOI
-
- Liu S., Liu S., Cai W., Pujol S., Kikinis R., Feng D. Early diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease with deep learning; Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE 11th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI); Beijing, China. 29 April–2 May 2014; pp. 1015–1018.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

