Modeling the dynamic behavior of biochemical regulatory networks
- PMID: 30502409
- PMCID: PMC6369921
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jtbi.2018.11.034
Modeling the dynamic behavior of biochemical regulatory networks
Abstract
Strategies for modeling the complex dynamical behavior of gene/protein regulatory networks have evolved over the last 50 years as both the knowledge of these molecular control systems and the power of computing resources have increased. Here, we review a number of common modeling approaches, including Boolean (logical) models, systems of piecewise-linear or fully non-linear ordinary differential equations, and stochastic models (including hybrid deterministic/stochastic approaches). We discuss the pro's and con's of each approach, to help novice modelers choose a modeling strategy suitable to their problem, based on the type and bounty of available experimental information. We illustrate different modeling strategies in terms of some abstract network motifs, and in the specific context of cell cycle regulation.
Keywords: Bifurcation theory; Dynamic models; Logical models; Molecular regulatory networks; Piecewise-linear odes; Signaling motifs; Stochastic models.
Copyright © 2018 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
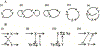
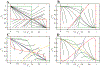
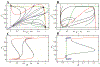

References
-
- Ahmadian M, Wang S, Tyson J, Cao Y, 2017. Hybrid ODE/SSA Model of the Budding Yeast Cell Cycle Control Mechanism with Mutant Case Study. Acm-Bcb’ 2017: Proceedings of the 8th Acm International Conference on Bioinformatics, Computational Biology,and Health Informatics, 464–473, doi: 10.1145/3107411.3107437. - DOI
-
- Alon U, 2007. An introduction to systems biology : design principles of biological circuits. Chapman & Hall/CRC, Boca Raton, FL.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

